
كيف تقوم علامات RFID بتخزين البيانات؟
جدول المحتويات
مقدمة
فهم هذه العملية ليس مجرد مسألة أكاديمية. بالنسبة للمهندسين الذين يصممون سلاسل التوريد الذكية، والمطورين الذين يبنون تطبيقات مدمجة مع تقنية RFID، ومديري تكنولوجيا المعلومات الذين يشرفون على تتبع الأصول على نطاق واسع، فإن الآليات الأساسية لذاكرة RFID وترميز البيانات وبروتوكولات الأمان تعتبر حاسمة للأداء وقابلية التشغيل البيني وسلامة البيانات.

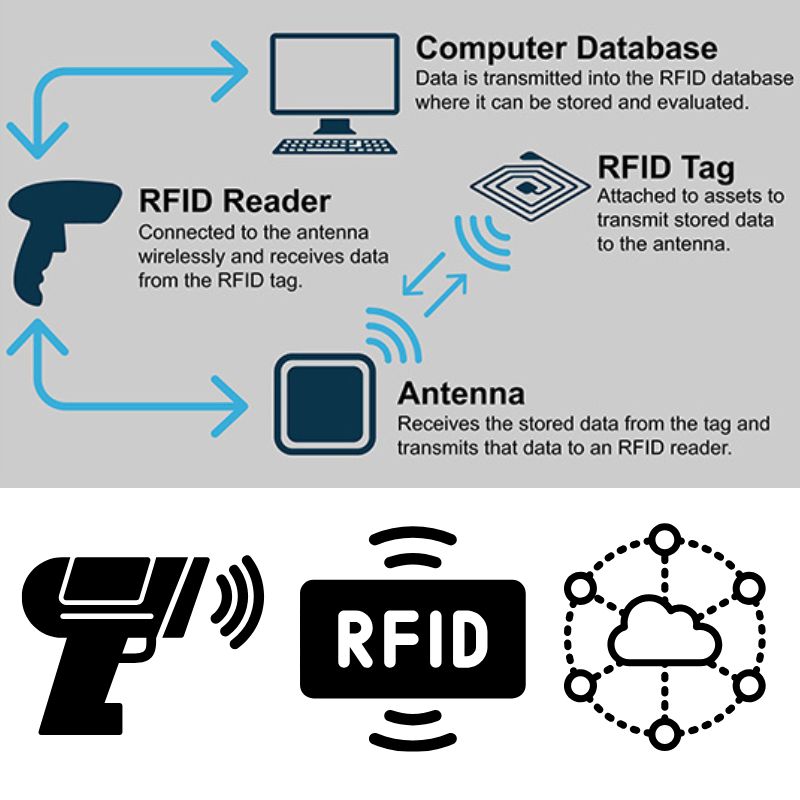
ما هو RFID وكيف يعمل؟
ما هو RFID؟
RFID (تحديد الهوية بواسطة الترددات الراديوية) هي تقنية لاسلكية تحدد وتتتبع الأجسام تلقائيًا باستخدام المجالات الكهرومغناطيسية. على عكس الباركود، لا تحتاج تقنية RFID إلى خط رؤية مباشر ويمكنها تخزين المزيد من البيانات مباشرة على العلامة.
المكونات الرئيسية لنظام RFID
- علامة RFID (جهاز إرسال واستقبال): شريحة وهوائي مدمجان في ملصق أو جسم يخزن البيانات.
- قارئ RFID (المستجوب): يرسل إشارة لاسلكية لتنشيط العلامة واستقبال بياناتها.
- البرمجيات الوسيطة/برمجيات النظام: تعالج البيانات وتخزنها وتوجهها إلى قواعد البيانات أو التطبيقات.
كيف يعمل نقل البيانات
عندما يصدر قارئ RFID إشارة تردد راديوي، تلتقطها هوائي العلامة وتزود الشريحة بالطاقة (إذا كانت سلبية). ثم تقوم الشريحة بتعديل البيانات المخزنة وإرسالها إلى القارئ. يختلف هذا الاتصال حسب التردد:
- LF (تردد منخفض): مدى قصير، جيد لتتبع الحيوانات.
- HF (التردد العالي): شائع في NFC والبطاقات الذكية.
- UHF (التردد فوق العالي): نطاق أطول، سرعات قراءة أسرع – مثالي للوجستيات.
نصيحة هندسية: تُستخدم العلامات UHF السلبية بشكل شائع في سلاسل التوريد الصناعية لأنها منخفضة التكلفة ويمكنها الإرسال لمسافات تصل إلى عدة أمتار.
دليل المبتدئين لبرمجة علامات RFID
يمكن لبرمجة علامات RFID أن تفتح إمكانات قوية — من تخصيص بيانات المنتج إلى تمكين التحكم الآمن في الوصول. على الرغم من توفر العديد من الأدوات والأساليب، فإن الطريقة المحددة تعتمد على نوع العلامة والتردد والتطبيق.
نحن نعمل حاليًا على أمثلة أكواد تم التحقق منها وإرشادات عملية لبرمجة علامات RFID بأمان وفعالية. سيتضمن هذا القسم قريبًا ما يلي:
- دروس عملية لاستخدام Arduino مع وحدات RFID.
- ترميز البيانات باستخدام TagWriter (Android) لـ علامات متوافقة مع NFC.
- استخدام مجموعات أدوات تطوير البرامج RFID وكتاب الطاولة لتطبيقات المؤسسات.
- نصائح حول اختيار تنسيق الذاكرة المناسب (ASCII، HEX، EPC).
هل تريد البدء الآن؟ نوصيك بالاطلاع على هذه الموارد في الوقت الحالي:
- تطبيق NXP TagWriter– ترميز NFC لنظام Android
- مكتبة MFRC522 Arduino على GitHub– مكتبة قارئ RFID مفتوحة المصدر
- [مجموعة أدوات تطوير البرامج أو أدوات المطورين الخاصة بمورد الأجهزة] لطرازات قارئات محددة
هل تحتاج إلى مساعدة في كتابة البيانات على بطاقات RFID الخاصة بك أو في اختيار الأدوات المتوافقة؟ اتصل بفريقنا الفني للدعم الشخصي
كيف تخزن علامات RFID البيانات داخليًا
في جوهرها، علامة RFID هي جهاز تخزين صغير يحتوي على بنوك ذاكرة محددة. فهم تخطيط الذاكرة الداخلية أمر بالغ الأهمية عند التخطيط لنوع البيانات التي سيتم تخزينها وكميتها.
أنواع الذاكرة في علامات RFID
- ROM (ذاكرة القراءة فقط): بيانات مكتوبة أثناء التصنيع. لا يمكن تغييرها.
- EEPROM (قابلة للمسح كهربائيًا): قابلة لإعادة الكتابة؛ تستخدم بشكل شائع في تقنية RFID الحديثة.
- ذاكرة الوصول العشوائي (RAM): ذاكرة تخزين مؤقتة، غالبًا ما تستخدم أثناء المعاملات النشطة.
أنواع الذاكرة الشائعة
- للقراءة فقط (RO): لا يمكن تغييرها. تُستخدم للمعرفات الثابتة.
- قراءة/كتابة (RW): يمكن تعديلها باستخدام قارئات متوافقة.
- WORM (الكتابة مرة واحدة، القراءة عدة مرات): بمجرد البرمجة، يتم قفل البيانات.
بنوك الذاكرة في علامات EPCglobal Gen2 (UHF)
| بنك الذاكرة | المحتويات | قابل للكتابة؟ |
|---|---|---|
| شهادة أداء الطاقة | معرف المنتج (96-128 بت عادةً) | ✅ |
| TID | معرف فريد للعلامة/الرقاقة | ❌ |
| ذاكرة المستخدم | بيانات خاصة بالتطبيق | ✅ |
| محجوز | كلمات المرور لأوامر الوصول/الإيقاف | ✅ (مقيد) |
أفضل الممارسات: استخدم EPC لمعرفات SKU أو المنتجات، وذاكرة المستخدم للبيانات الإضافية مثل الطوابع الزمنية أو أرقام الدفعات أو البيانات الوصفية اللوجستية.
تنسيق البتات والكتل
- تنقسم الذاكرة إلى كتل (16 أو 32 بت).
- يمكن معالجة كل كتلة على حدة.
- يجب أن يحترم ترميز البيانات حجم الكتلة ومواصفات العلامة.
مثال: علامة ذات ذاكرة مستخدم سعة 512 بت تحتوي على 64 بايت متاحة للتشفير – قم بتخطيط بنية البيانات وفقًا لذلك.
ما مدى أمان البيانات الموجودة على بطاقات RFID؟
مع تزايد اندماج تقنية RFID في سلاسل التوريد والمنتجات الاستهلاكية، أصبح أمن البيانات أحد أهم الشواغل. إن فهم كيفية حماية علامات RFID للبيانات — وكيفية تعريضها للخطر في بعض الأحيان — أمر بالغ الأهمية لضمان أمان عمليات النشر.
هل يمكن اختراق علامات RFID؟
نعم — ولكن السياق مهم. في حين أن العلامات الأساسية منخفضة التكلفة يمكن استنساخها أو نسخها، فإن معظم أنظمة RFID الحديثة تطبق طبقات متعددة من الأمان، بما في ذلك التحكم في الوصول والتشفير.
آليات الأمان في علامات RFID
| ميزة الأمان | وصف | مستوى الحماية |
|---|---|---|
| حماية كلمة المرور | يمنع القراءة/الكتابة غير المصرح بها | واسطة |
| بتات التحكم في الوصول | تحديد أذونات القراءة/الكتابة لكل بنك ذاكرة | عالي |
| التشفير (AES، DES) | تستخدم في العلامات عالية الأمان (مثل الخدمات المصرفية والتحكم في الوصول) | عالية جداً |
| أوامر القتل | تعطيل علامة بشكل دائم لمنع إساءة الاستخدام | سياقي |
الضعفات الشائعة
- التنصت: يقوم المهاجمون باعتراض اتصالات قارئ العلامات.
- الاستنساخ: نسخ بيانات العلامة إلى علامة أخرى.
- هجمات إعادة التشغيل: إعادة استخدام بيانات الإرسال الملتقطة.
أفضل الممارسات لنشر تقنية RFID بشكل آمن
- استخدم علامات محمية بكلمة مرور أو مشفرة للبيانات الهامة.
- تجنب تخزين المعلومات الحساسة مباشرة على العلامات — قم بتخزين المراجع أو المعرفات فقط.
- تنفيذ قواعد بيانات خلفية آمنة للتحقق من صحة بيانات العلامات.
- حماية أو تعطيل العلامات بعد استخدامها في سياقات حساسة.
ما مقدار البيانات التي يمكن أن تخزنها علامات RFID؟
أحد الأسئلة الأكثر شيوعًا التي يطرحها المهندسون هو:
“ما مقدار البيانات التي يمكنني تخزينها على علامة RFID؟”
سعات ذاكرة RFID النموذجية
| نوع العلامة | نطاق الذاكرة | حالة الاستخدام |
|---|---|---|
| التردد المنخفض (LF) | 64-256 بت | بطاقات هوية الحيوانات، بطاقات الدخول |
| التردد العالي (HF/NFC) | 128-4096 بت | البطاقات الذكية، المخزون |
| التردد فوق العالي (UHF) | 96–8192 بت | اللوجستيات، التتبع الصناعي |
| تقنية تحديد الهوية بموجات الراديو النشطة | 32 كيلوبايت+ | بيانات المستشعرات، حمولات كبيرة |
العوامل التي تؤثر على السعة
- تكرار العلامة ونموذج الرقاقة.
- استخدام التشفير أو بيانات المجموع الاختباري.
- نوع التطبيق (على سبيل المثال، ترميز EPC مقابل ترميز محدد من قبل المستخدم).
ما نوع البيانات التي يتم تخزينها عادةً؟
- معرفات المنتجات (EPC)
- أرقام الدُفعات أو الكميات
- الطوابع الزمنية
- بيانات المستشعر (درجة الحرارة والضغط) في العلامات النشطة
نصيحة: قم بتخزين الحد الأدنى من البيانات الضرورية على العلامة واربطها بقواعد البيانات الخارجية للحصول على التفاصيل. هذا يقلل من متطلبات الذاكرة ويحسن الأداء.
RFID السلبي مقابل RFID النشط: مقارنة قدرات تخزين البيانات
يؤثر الاختيار بين RFID السلبي والنشط على التكلفة وسعة البيانات والنطاق.
| ميزة | تقنية تحديد الهوية بموجات الراديو السلبية | تقنية تحديد الهوية بموجات الراديو النشطة |
|---|---|---|
| مصدر الطاقة | مدعوم من القارئ | بطارية مدمجة |
| سعة البيانات | 96–8192 بت | 32 كيلوبايت أو أكثر |
| يتراوح | حتى 10 أمتار | حتى 100 متر |
| عمر | غير محدود (بدون بطارية) | محدود بعمر البطارية |
| يكلف | <$0.10 لكل علامة | $10–$50 لكل علامة |
أيهما يجب أن تختار؟
- العلامات السلبية: مثالية للمخزون والتجزئة والتحكم في الوصول.
- العلامات النشطة: الأفضل لتتبع الأصول في الوقت الفعلي، واللوجستيات، وأجهزة استشعار إنترنت الأشياء.
أمثلة من الواقع — ما هي البيانات المخزنة على بطاقات RFID؟
دعونا نلقي نظرة على كيفية عمل تخزين بيانات RFID في الصناعات الحقيقية.
في تجارة التجزئة
- رقم تعريف المنتج (EPC)
- الأسعار ورموز المنتجات وأرقام الدفعات
- موقع الرف أو بيانات الفئة
في الرعاية الصحية
- رقم هوية المريض
- معلومات عن جرعة الدواء
- تتبع المعدات
في مجال الخدمات اللوجستية
- معرفات الشحنات، الطوابع الزمنية
- رموز الحاويات
- تتبع المسار ونقاط التفتيش
في تتبع الحيوانات
- رقم تعريف السلالة، سجلات التطعيمات
- GPS أو معرفات الموقع (في العلامات النشطة)
رؤية احترافية: تربط معظم أنظمة المؤسسات معرفات العلامات بقواعد البيانات السحابية (ERP، WMS)، مما يقلل من الحاجة إلى تخزين مجموعات بيانات كبيرة على العلامة نفسها.
كيفية كتابة البيانات على بطاقات RFID (عملية الترميز)
متطلبات الأجهزة
- وحدة كتابة أو قراءة/كتابة RFID
- البرامج المتوافقة (TagWriter أو Arduino IDE أو SDKs)
- العلامات المتوافقة مع RFID
سير عمل الترميز النموذجي
- قم بتوصيل الكاتب بالنظام أو وحدة التحكم الدقيقة.
- حدد نوع العلامة وترددها (LF، HF، UHF).
- اختر تنسيق البيانات (EPC أو HEX أو ASCII).
- اكتب البيانات على العلامة باستخدام أوامر البرنامج.
- تحقق من البيانات باستخدام وظيفة القراءة.
تنسيقات الترميز الشائعة
| شكل | مثال | حالة الاستخدام |
|---|---|---|
| EPC (96 بت) | 300833B2DDD9014000000001 | رقم المنتج |
| HEX | 0xA1B2C3D4 | تخزين البيانات الثنائية |
| ASCII | “ITEM00123” | سلاسل قابلة للقراءة |
هل تحتاج إلى مشفرات صناعية؟ تصفح منتجاتنا مجموعات أجهزة كتابة RFID لأنظمة UHF و NFC.
RFID مقابل الباركود مقابل NFC: مقارنة تخزين البيانات
| ميزة | تقنية تحديد الهوية بموجات الراديو | الباركود | تقنية الاتصال قريب المدى |
|---|---|---|---|
| سعة البيانات | 64 بت – 32 كيلوبايت | 12-20 حرفًا | حتى 4 كيلوبايت |
| قراءة المدى | 1-100 متر | 0.2-1 م | 0-10 سم |
| قابلة لإعادة الكتابة؟ | نعم | لا | نعم |
| القراءات المتزامنة | مئات العلامات | واحدا تلو الآخر | واحدا تلو الآخر |
| متانة | عالي | قليل | واسطة |
النقاط الرئيسية
- RFID: الأفضل لبيئات البيانات عالية السرعة والكثافة.
- الباركود: بسيط ورخيص بالنسبة للهويات الثابتة.
- NFC: مثالي للتفاعلات الآمنة قصيرة المدى (مثل المدفوعات).
هل تفكر في الترقية من الباركود إلى RFID؟ احصل على عرض أسعار مجاني للتنفيذ.
أسئلة وأجوبة حول تخزين بيانات RFID
هل يمكن إعادة كتابة علامات RFID؟
نعم — تدعم معظم بطاقات HF و UHF دورات كتابة متعددة حتى يحدث تلف في الذاكرة.
كم من الوقت تبقى البيانات على بطاقة RFID؟
تصل إلى 10 سنوات أو أكثر للعلامات السلبية، اعتمادًا على جودة الرقاقة.
هل بيانات RFID مشفرة؟
تدعم بعض العلامات تشفير AES/DES؛ بينما تعتمد أخرى على الحماية بكلمة مرور.
هل يمكنني برمجة علامات RFID باستخدام هاتف ذكي؟
نعم، إذا كانت متوافقة مع تقنية NFC (13.56 ميجاهرتز) وكان هاتفك مزودًا بقارئ NFC.
ما هو البرنامج المستخدم لكتابة علامات RFID؟
TagWriter أو Arduino IDE (مع المكتبات) أو SDKs الخاصة بالشركة المصنعة.
مستقبل تخزين بيانات RFID
يكمن مستقبل تقنية RFID في التقاطع بين إنترنت الأشياء والذكاء الاصطناعي — حيث لا تقتصر وظيفة العلامات على تخزين البيانات فحسب، بل تتواصل بشكل فعال مع أنظمة السحابة وأجهزة الاستشعار.
الابتكارات الناشئة
- زيادة كثافة الذاكرة باستخدام تقنية micro-EEPROM
- أجهزة استشعار مدمجة تخزن بيانات درجة الحرارة أو الحركة
- تحليلات RFID مدعومة بالذكاء الاصطناعي لأتمتة عملية اتخاذ القرار
- تتبع أصالة المنتجات المدعوم بتقنية البلوك تشين
الخلاصة: تلخيص كل ما سبق
علامات RFID هي ناقلات بيانات صغيرة الحجم ولكنها قوية وتشكل أساس الأتمتة الحديثة.
من هياكل الذاكرة الأساسية إلى التشفير المتقدم، فإن فهم كيفية تخزين وانتقال البيانات بواسطة علامات RFID يمكّن المهندسين والمطورين والشركات من بناء أنظمة أكثر ذكاءً وأمانًا.
النقاط الرئيسية:
- اختر أنواع العلامات بناءً على النطاق والسعة والتطبيق.
- استخدم تشفيرًا آمنًا ومحميًا بكلمة مرور للبيانات الحساسة.
- دمج RFID مع أنظمة الخلفية من أجل قابلية التوسع.
هل تحتاج إلى مساعدة في تصميم أو برمجة نظام RFID الخاص بك؟
تواصل مع فريقنا للحصول على حلول RFID مخصصة، وتوريد الأجهزة، ودعم التنفيذ.

راي تشو
كتب هذا المقال راي تشو، وهو خبير في تكنولوجيا تحديد الهوية بموجات الراديو اللاسلكية يتمتع بخبرة تزيد عن 10 سنوات في هذا المجال.
تعليقات
المنتجات الساخنة

تقنية RFID في مجال الخدمات اللوجستية: كيفية القضاء على أخطاء التوجيه وعيوب ملصقات RFID
تعد تقنية RFID في مجال الخدمات اللوجستية أكثر من مجرد أداة لتسريع العمليات. فقد أصبحت جزءًا أساسيًا من طريقة عمل سلاسل التوريد الحديثة.

ما هي إدارة النفايات باستخدام تقنية RFID؟
تخيل مدينة حيث كل سلة مهملات تتحدث — ليس حرفياً — ولكن من خلال شريحة صغيرة تخبر النظام عندما تمتلئ، وعندما يتم إفراغها، وأين ذهبت. هذا ما تفعله إدارة النفايات باستخدام تقنية RFID اليوم.

ما هي أختام البراغي وتطبيقاتها؟ | الدليل الكامل
في مجال التجارة العالمية والخدمات اللوجستية العالمية، تلعب الأختام المزودة بمسامير دورًا حاسمًا في ضمان أمن البضائع والامتثال. صُممت هذه الأجهزة الصغيرة والقوية في نفس الوقت لقفل حاويات الشحن والمقطورات وأبواب الشحن بآلية واضحة للتلاعب.

ما هو واقي بطاقة RFID؟ الفوائد وحالات الاستخدام ودليل الشراء
إن تقنية RFID (تحديد الهوية بالترددات الراديوية) موجودة في كل مكان: في بطاقات الائتمان الخاصة بك، وشارات الهوية، وتصاريح العبور، ومفاتيح غرف الفنادق، وغيرها. إنها توفر السرعة والراحة، ولكنها أيضاً تفتح الباب أمام نوع جديد من السرقة الرقمية يسمى "القشط". وهنا يأتي دور واقي البطاقة بتقنية RFID.

أساور المعصم RFID للفعاليات: دليل الشراء بالجملة للمنظمين
أصبحت أساور المعصم التي تعمل بتقنية RFID للأحداث هي الحل المفضل للمنظمين الذين يحتاجون إلى دخول أسرع ومنع الاحتيال والمدفوعات غير النقدية في الحفلات الموسيقية والمهرجانات والأماكن الرياضية. على عكس التذاكر الورقية أو رموز الاستجابة السريعة، تستخدم هذه الأساور الذكية رقائق مدمجة لتبسيط الدخول وتأمين المعاملات وتحسين تجربة الضيوف.

كيف تعمل بطاقة RFID على الزجاج الأمامي على تحسين أنظمة التحكم في دخول المركبات ورسوم المرور
في عالم اليوم سريع الإيقاع، يجب أن يكون التعرف على المركبات سريعاً وآمناً وبدون تلامس. توفر بطاقة RFID على الزجاج الأمامي ذلك بالضبط - طريقة موثوقة لإدارة تحصيل رسوم المرور ومواقف السيارات والدخول من البوابات دون إيقاف المركبات.
العلامات
المدونات ذات الصلة

تقنية RFID في مجال الخدمات اللوجستية: كيفية القضاء على أخطاء التوجيه وعيوب ملصقات RFID
تعد تقنية RFID في مجال الخدمات اللوجستية أكثر من مجرد أداة لتسريع العمليات. فقد أصبحت جزءًا أساسيًا من طريقة عمل سلاسل التوريد الحديثة.

ما هي إدارة النفايات باستخدام تقنية RFID؟
تخيل مدينة حيث كل سلة مهملات تتحدث — ليس حرفياً — ولكن من خلال شريحة صغيرة تخبر النظام عندما تمتلئ، وعندما يتم إفراغها، وأين ذهبت. هذا ما تفعله إدارة النفايات باستخدام تقنية RFID اليوم.

ما هي أختام البراغي وتطبيقاتها؟ | الدليل الكامل
في مجال التجارة العالمية والخدمات اللوجستية العالمية، تلعب الأختام المزودة بمسامير دورًا حاسمًا في ضمان أمن البضائع والامتثال. صُممت هذه الأجهزة الصغيرة والقوية في نفس الوقت لقفل حاويات الشحن والمقطورات وأبواب الشحن بآلية واضحة للتلاعب.




