
Как RFID етикетите съхраняват данни?
Съдържание
Въведение
Разбирането на този процес не е само академично. За инженерите, които проектират интелигентни вериги за доставки, разработчиците, които създават приложения с интегрирана RFID технология, и ИТ мениджърите, които контролират проследяването на активи в голям мащаб, основните механизми на RFID паметта, кодирането на данни и протоколите за сигурност са от решаващо значение за производителността, оперативната съвместимост и целостта на данните.

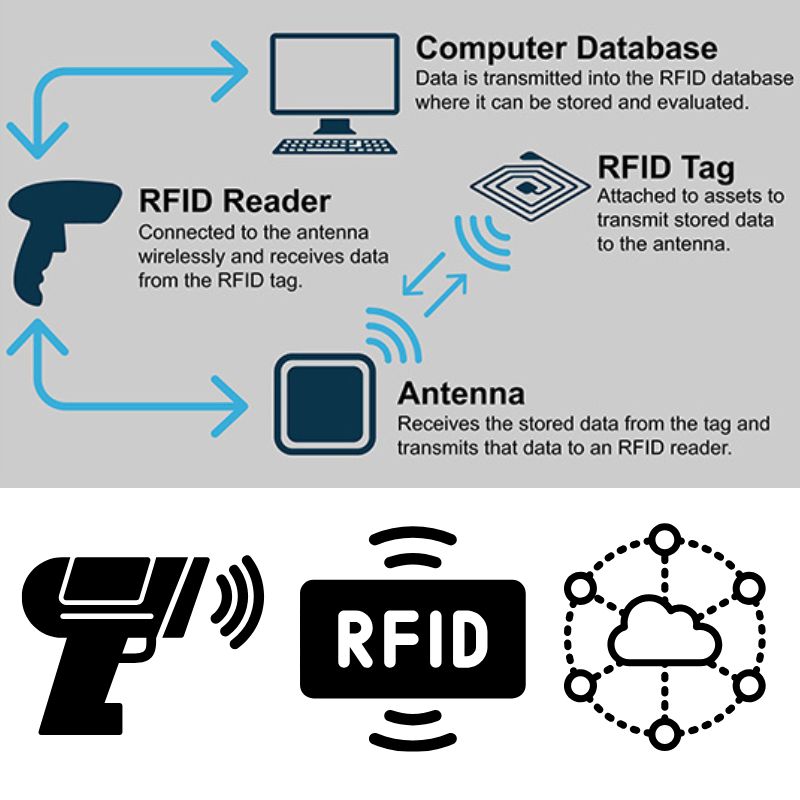
Какво е RFID и как работи?
Какво е RFID?
RFID (радиочестотна идентификация) е безжична технология, която автоматично идентифицира и проследява обекти, използвайки електромагнитни полета. За разлика от баркодовете, RFID не се нуждае от пряка видимост и може да съхранява повече данни директно на етикета.
Ключови компоненти на RFID система
- RFID етикет (Транспондер): Чип и антена, вградени в етикет или обект, които съхраняват данни.
- RFID четец (Интеррогатор): Изпраща радио сигнал, за да активира тага и да получи данните му.
- Средно софтуер/системно софтуер: Обработва, съхранява и препраща данни към бази данни или приложения.
Как работи предаването на данни
Когато RFID четецът излъчва радиочестотен сигнал, антената на етикета го улавя и захранва чипа (ако е пасивен). След това чипът модулира и изпраща съхранените данни обратно към четеца. Тази комуникация варира в зависимост от честотата:
- LF (ниска честота): къс обхват, подходящ за проследяване на животни.
- HF (висока честота): Често срещана в NFC и смарт карти.
- UHF (Ultra High Frequency): По-голям обхват, по-висока скорост на четене – идеален за логистика.
Инженерна препоръка: Пасивните UHF етикети се използват най-често в индустриалните вериги за доставки, защото са евтини и могат да предават сигнал на разстояние до няколко метра.
Наръчник за начинаещи за програмиране на RFID етикети
Програмирането на RFID етикети може да отключи мощни възможности — от персонализиране на продуктови данни до осигуряване на сигурен контрол на достъпа. Въпреки че са налични много инструменти и подходи, конкретният метод зависи от типа на етикета, честотата и приложението.
В момента работим върху проверени примери за код и практически указания за безопасно и ефективно програмиране на RFID етикети. Тази секция скоро ще включва:
- Практически уроци за използване на Arduino с RFID модули.
- Кодиране на данни с помощта на TagWriter (Android) за NFC-съвместими етикети.
- Използване на RFID SDK и настолни писалки за корпоративни приложения.
- Съвети за избор на подходящ формат на паметта (ASCII, HEX, EPC).
Искате да започнете веднага? Междувременно ви препоръчваме да разгледате следните ресурси:
- Приложение NXP TagWriter– NFC кодиране за Android
- Библиотека MFRC522 Arduino в GitHub– Библиотека с отворен код за RFID четци
- [SDK или инструменти за разработчици на вашия доставчик на хардуер] за конкретни модели четци
Нуждаете се от помощ при записването на данни на вашите RFID етикети или при избора на съвместими инструменти? Свържете се с нашия технически екип за персонализирана поддръжка.
Как RFID етикетите съхраняват данни вътрешно
В основата си RFID етикетът е малко устройство за съхранение с конкретни памети. Разбирането на вътрешната структура на паметта е от решаващо значение при планирането на вида и обема на данните, които ще се съхраняват.
Видове памет в RFID етикети
- ROM (памет само за четене): Данни, записани по време на производството. Не могат да бъдат променяни.
- EEPROM (Electrically Erasable): Презаписваема; най-често използвана в съвременните RFID.
- RAM: Временно съхранение, често използвано по време на активни транзакции.
Общи типове памети
- Само за четене (RO): Не може да бъде променяно. Използва се за фиксирани идентификатори.
- Четене/запис (RW): Може да се модифицира с съвместими четци.
- WORM (Write Once, Read Many – записва се веднъж, чете се многократно): След като бъдат програмирани, данните се заключват.
Памети в EPCglobal Gen2 тагове (UHF)
| Банка за памет | Съдържание | Записваем? |
|---|---|---|
| EPC | Идентификационен номер на продукта (обикновено 96-128 бита) | ✅ |
| TID | Уникален идентификатор на етикет/чип | ❌ |
| Потребителска памет | Данни, специфични за приложението | ✅ |
| Запазено | Пароли за команди за достъп/унищожаване | ✅ (Ограничено) |
Най-добра практика: Използвайте EPC за SKU или идентификатори на продукти и потребителска памет за допълнителни данни като времеви отметки, номера на партиди или метаданни за логистика.
Форматиране на битове и блокове
- Паметта е разделена на блокове (16 или 32 бита).
- Всеки блок може да бъде адресиран индивидуално.
- Кодирането на данните трябва да спазва спецификациите за размер на блока и етикетите.
Пример: Етикет с 512 бита потребителска памет разполага с 64 байта за кодиране – планирайте структурата на данните си съответно.
Колко сигурни са данните на RFID етикетите?
С все по-широкото внедряване на RFID технологията в веригите за доставки и потребителските продукти, сигурността на данните се превърна в основен проблем. Разбирането на това как RFID етикетите защитават — а понякога и разкриват — данните е от решаващо значение за сигурното им внедряване.
Могат ли RFID етикетите да бъдат хакнати?
Да, но контекстът е важен. Докато основните евтини етикети могат да бъдат клонирани или сканирани, повечето съвременни RFID системи прилагат многослойни мерки за сигурност, включително контрол на достъпа и криптиране.
Механизми за сигурност в RFID етикетите
| Функция за сигурност | Описание | Ниво на защита |
|---|---|---|
| Защита с парола | Блокира неразрешени четения/записи | Среден |
| Битове за контрол на достъпа | Дефиниране на разрешения за четене/записване за всеки паметен блок | високо |
| Криптиране (AES, DES) | Използва се в етикети с висока степен на сигурност (например в банковото дело, контрол на достъпа) | Много висока |
| Команди за убиване | Деактивирайте трайно етикет, за да предотвратите злоупотреба | Контекстуален |
Често срещани уязвимости
- Подслушване: Нападателите прехващат комуникацията между четеца на етикети.
- Клониране: Копиране на данни от етикет върху друг етикет.
- Атаки с повторно възпроизвеждане: Повторна употреба на заснети данни от предаване.
Най-добри практики за безопасно внедряване на RFID
- Използвайте защитени с парола или криптирани етикети за критични данни.
- Избягвайте да съхранявате чувствителна информация директно на етикетите — съхранявайте само препратки или идентификатори.
- Внедрете сигурни бекенд бази данни за валидиране на данните от таговете.
- Защитавайте или деактивирайте таговете след употреба в чувствителни контексти.
Колко данни могат да съхраняват RFID етикетите?
Един от най-често задаваните въпроси от инженерите е:
“Колко данни мога да съхранявам на RFID етикет?”
Типични капацитети на RFID паметта
| Тип етикет | Обхват на паметта | Случай на употреба |
|---|---|---|
| Ниска честота (LF) | 64–256 бита | Идентификационни номера на животни, карти за достъп |
| Висока честота (HF/NFC) | 128–4096 бита | Смарт карти, инвентар |
| Свръхвисока честота (UHF) | 96–8192 бита | Логистика, проследяване в промишлеността |
| Активен RFID | 32 KB+ | Данни от сензори, големи товари |
Фактори, които влияят върху капацитета
- Честота на таговете и модел на чипа.
- Използване на криптиране или контролна сума на данните.
- Тип на приложението (например EPC кодиране срещу дефинирано от потребителя).
Какъв тип данни обикновено се съхраняват?
- Идентификатори на продукти (EPC)
- Номера на партиди или серии
- Времеви отметки
- Данни от сензори (температура, налягане) в активни тагове
Съвет: Съхранявайте само минимално необходимите данни на етикета и се свържете с външни бази данни за подробности. Това намалява изискванията за памет и подобрява производителността.
Пасивен срещу активен RFID: Сравнение на възможностите за съхранение на данни
Изборът между пасивен и активен RFID оказва влияние върху цената, капацитета на данните и обхвата.
| Характеристика | Пасивна RFID | Активен RFID |
|---|---|---|
| Източник на захранване | Задвижвано от четец | Вградена батерия |
| Капацитет на данни | 96–8192 бита | 32 KB или повече |
| Обхват | До 10 м | До 100 м |
| Продължителност на живота | Неограничен (без батерия) | Ограничено от живота на батерията |
| цена | <$0,10 на етикет | $10–$50 на етикет |
Кое да изберете?
- Пасивни етикети: Идеални за инвентаризация, търговия на дребно, контрол на достъпа.
- Активни тагове: Най-подходящи за проследяване на активи в реално време, логистика, IoT сензори.
Примери от реалния свят — какви данни се съхраняват на RFID етикетите?
Нека разгледаме как работи съхранението на данни чрез RFID в реални индустрии.
В търговията на дребно
- Идентификационен номер на продукта (EPC)
- Цени, SKU и номера на партидите
- Данни за местоположението на рафта или категорията
В здравеопазването
- Идентификационен номер на пациента
- Информация за дозировката на лекарствата
- Проследяване на оборудването
В логистиката
- Идентификационни номера на пратки, времеви отметки
- Кодове на контейнерите
- Проследяване на маршрута и контролните точки
В проследяването на животни
- Идентификационен номер на породата, записи за ваксини
- GPS или идентификатори на местоположението (в активни тагове)
Професионален поглед: Повечето корпоративни системи свързват идентификаторите на етикетите с облачни бази данни (ERP, WMS), което намалява необходимостта от съхранение на големи масиви от данни върху самия етикет.
Как се записват данните в RFID етикетите (процес на кодиране)
Изисквания към хардуера
- RFID записващо устройство или модул за четене/записване
- Съвместим софтуер (TagWriter, Arduino IDE или SDK)
- RFID-съвместими етикети
Типичен работен процес на кодиране
- Свържете вашия писател към системата или микроконтролера.
- Изберете типа и честотата на етикета (LF, HF, UHF).
- Изберете формат на данните (EPC, HEX или ASCII).
- Запишете данните на етикета с помощта на софтуерни команди.
- Проверете данните с помощта на функция за четене.
Общи формати за кодиране
| Форматиране | Пример | Случай на употреба |
|---|---|---|
| EPC (96-битов) | 300833B2DDD9014000000001 | Идентификационен номер на продукта |
| HEX | 0xA1B2C3D4 | Съхранение на двоични данни |
| ASCII | “ITEM00123” | Четливи низове |
Нуждаете се от енкодери с промишлено качество? Разгледайте нашата Комплекти за RFID записващи устройства за UHF и NFC системи.
RFID срещу баркод срещу NFC: сравнение на съхранението на данни
| Характеристика | RFID | Баркод | NFC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Капацитет на данни | 64 бита – 32 KB | 12–20 символа | До 4 KB |
| Обхват на четене | 1–100 м | 0,2–1 м | 0-10 см |
| Може да се презаписва? | да | не | да |
| Едновременно четене | Стотици етикети | Един по един | Един по един |
| Издръжливост | високо | ниско | Среден |
Ключови изводи
- RFID: Най-подходящ за високоскоростни среди с голям обем данни.
- Баркод: Прост и евтин за статични идентификатори.
- NFC: Идеален за сигурни взаимодействия на късо разстояние (например плащания).
Мислите да преминете от баркодове към RFID? Получете безплатна оферта за внедряване.
Често задавани въпроси за съхранението на данни чрез RFID
Могат ли RFID етикетите да бъдат презаписани?
Да — повечето HF и UHF етикети поддържат множество цикли на запис, докато не се износи паметта.
Колко дълго се съхраняват данните на RFID етикета?
До 10 години или повече за пасивни етикети, в зависимост от качеството на чипа.
Данните от RFID криптирани ли са?
Някои тагове поддържат AES/DES криптиране, а други разчитат на защита с парола.
Мога ли да програмирам RFID етикети със смартфон?
Да, ако са съвместими с NFC (13,56 MHz) и телефонът ви има NFC четец.
Какъв софтуер се използва за записване на RFID етикети?
TagWriter, Arduino IDE (с библиотеки) или SDK на производителя.
Бъдещето на съхранението на RFID данни
Бъдещето на RFID се намира на пресечната точка между IoT и AI — където етикетите не само съхраняват данни, но и активно комуникират с облачни системи и сензори.
Нови иновации
- Повишена плътност на паметта с микро-EEPROM технология
- Интегрирани сензори, които съхраняват данни за температурата или движението
- AI-базирани RFID анализи за автоматизиране на вземането на решения
- Проследимост, подкрепена от блокчейн, за автентичност на продуктите
Заключение: обобщение
RFID етикетите са малки, но мощни носители на данни, които са в основата на съвременната автоматизация.
От основни структури на паметта до усъвършенствано криптиране, разбирането на начина, по който RFID етикетите съхраняват и предават данни, дава възможност на инженерите, разработчиците и бизнеса да създават по-интелигентни и по-сигурни системи.
Ключови изводи:
- Изберете типове етикети въз основа на обхват, капацитет и приложение.
- Използвайте сигурно, защитено с парола кодиране за чувствителни данни.
- Интегрирайте RFID с бекенд системи за мащабируемост.
Нуждаете се от помощ при проектирането или програмирането на вашата RFID система?
Свържете се с нашия екип за персонализирани RFID решения, доставка на хардуер и поддръжка при внедряването.

Рей Джоу
Тази статия е написана от Рей Джоу, експерт по технологиите за радиочестотна идентификация с повече от 10 години опит в индустрията.
Коментари
Горещи продукти

RFID в логистиката: Как да се елиминират грешките при маршрутизирането и повредите на RFID етикетите
RFID в логистиката е повече от просто инструмент за ускоряване на процесите. Тя се е превърнала в ключова част от начина, по който функционират съвременните вериги за доставки.

Какво е RFID управление на отпадъците
Представете си град, в който всяка кошница за боклук „говори“ – не буквално, а чрез малък чип, който информира системата кога е пълна, кога е изпразнена и къде е отишла. Това е, което прави RFID управлението на отпадъците днес.

Какво представляват болтовите уплътнения и техните приложения? | Пълно ръководство
В глобалната търговия и логистика болтовите пломби играят решаваща роля за гарантиране на сигурността на товара и спазването на изискванията. Тези малки, но мощни устройства са предназначени за заключване на транспортни контейнери, ремаркета и товарни врати с механизъм, който не позволява проникване в тях.

Какво е RFID протектор за карти? Предимства, случаи на употреба и ръководство за купуване
Технологията RFID (радиочестотна идентификация) е навсякъде: в кредитните ви карти, личните карти, транзитните пропуски, ключовете за хотелски стаи и др. Тя предлага бързина и удобство, но също така отваря вратата за нов вид цифрова кражба, наречена "скимиране". Ето къде се намесва RFID протекторът за карти.

RFID гривни за събития: Ръководство за купуване на големи количества за организаторите
RFID гривните за събития се превръщат в решение за организаторите, които се нуждаят от по-бързо влизане, предотвратяване на измами и безкасови плащания на концерти, фестивали и спортни обекти. За разлика от хартиените билети или QR кодовете, тези интелигентни гривни използват вградени чипове за рационализиране на достъпа, осигуряване на трансакции и подобряване на преживяването на гостите.

Как RFID етикетът на предното стъкло подобрява системите за контрол на достъпа до превозни средства и за събиране на пътни такси
В днешния динамичен свят идентификацията на превозните средства трябва да бъде бърза, сигурна и безконтактна. RFID етикетът на предното стъкло осигурява точно това - надежден начин за управление на събирането на пътни такси, паркирането и достъпа до затворени пространства, без да се налага спиране на превозните средства.
Етикети
СВЪРЗАНИ БЛОГОВЕ

RFID в логистиката: Как да се елиминират грешките при маршрутизирането и повредите на RFID етикетите
RFID в логистиката е повече от просто инструмент за ускоряване на процесите. Тя се е превърнала в ключова част от начина, по който функционират съвременните вериги за доставки.

Какво е RFID управление на отпадъците
Представете си град, в който всяка кошница за боклук „говори“ – не буквално, а чрез малък чип, който информира системата кога е пълна, кога е изпразнена и къде е отишла. Това е, което прави RFID управлението на отпадъците днес.

Какво представляват болтовите уплътнения и техните приложения? | Пълно ръководство
В глобалната търговия и логистика болтовите пломби играят решаваща роля за гарантиране на сигурността на товара и спазването на изискванията. Тези малки, но мощни устройства са предназначени за заключване на транспортни контейнери, ремаркета и товарни врати с механизъм, който не позволява проникване в тях.




