
RFID 태그는 어떻게 데이터를 저장하나요?
목차
소개
이 과정을 이해하는 것은 단순한 학문적 지식이 아닙니다. 스마트 공급망을 설계하는 엔지니어, RFID 통합 애플리케이션을 구축하는 개발자, 대규모 자산 추적을 관리하는 IT 관리자에게 RFID 메모리, 데이터 인코딩 및 보안 프로토콜의 기본 메커니즘은 성능, 상호 운용성 및 데이터 무결성을 위해 매우 중요합니다.

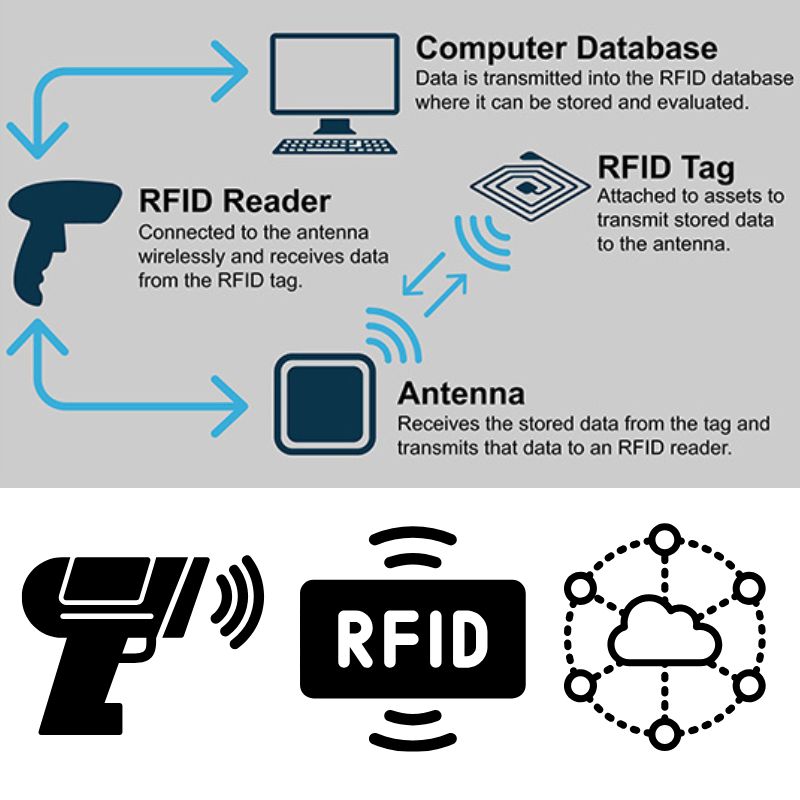
RFID란 무엇이고 어떻게 작동하나요?
RFID란 무엇인가?
RFID(무선 주파수 식별)은 전자기장을 이용해 물체를 자동으로 식별하고 추적하는 무선 기술입니다. 바코드와 달리 RFID는 직접적인 시야가 필요하지 않으며 태그에 더 많은 데이터를 직접 저장할 수 있습니다.
RFID 시스템의 주요 구성 요소
데이터 전송의 작동 방식
RFID 리더기가 무선 주파수 신호를 방출하면 태그의 안테나가 이를 수신하여 칩에 전원을 공급합니다(수동형 태그의 경우). 이후 칩은 저장된 데이터를 변조하여 리더기로 다시 전송합니다. 이 통신 방식은 주파수에 따라 달라집니다:
- LF (저주파): 단거리, 동물 추적에 적합.
- HF(고주파): NFC 및 스마트 카드에서 흔히 사용됩니다.
- UHF(초고주파): 더 긴 거리, 더 빠른 읽기 속도 – 물류에 이상적입니다.
엔지니어링 팁: 수동형 UHF 태그는 비용이 저렴하고 수 미터까지 전송이 가능하기 때문에 산업용 공급망에서 가장 흔히 사용됩니다.
초보자를 위한 RFID 태그 프로그래밍 가이드
RFID 태그 프로그래밍은 제품 데이터 맞춤 설정부터 안전한 접근 제어 구현에 이르기까지 강력한 기능을 가능하게 합니다. 다양한 도구와 접근법이 존재하지만, 구체적인 방법은 태그 유형, 주파수 및 적용 분야에 따라 달라집니다.
현재 RFID 태그를 안전하고 효과적으로 프로그래밍하기 위한 검증된 코드 예제와 실용적인 단계별 안내를 준비 중입니다. 이 섹션에는 곧 다음 내용이 포함될 예정입니다:
- 아두이노와 RFID 모듈 사용을 위한 실습 튜토리얼.
- TagWriter(Android)를 사용한 데이터 인코딩 NFC 호환 태그.
- RFID SDK 및 데스크탑 라이터를 활용한 기업용 애플리케이션.
- 적절한 메모리 형식(ASCII, HEX, EPC) 선택을 위한 팁.
지금 시작하시겠습니까? 그동안 다음 자료를 살펴보시길 권합니다:
- NXP 태그라이터 앱– 안드로이드용 NFC 인코딩
- MFRC522 아두이노 라이브러리 GitHub– 오픈소스 RFID 리더 라이브러리
- [특정 리더기 모델용 하드웨어 공급업체의 SDK 또는 개발자 도구]
RFID 태그에 데이터를 기록하거나 호환 가능한 도구를 선택하는 데 도움이 필요하신가요? 기술팀에 문의하십시오 를 통해 맞춤형 지원을 받을 수 있습니다.
RFID 태그가 내부적으로 데이터를 저장하는 방식
RFID 태그의 핵심은 특정 메모리 뱅크를 가진 초소형 저장 장치입니다. 어떤 종류의 데이터를 저장할지, 그리고 얼마나 저장할지 계획할 때 내부 메모리 레이아웃을 이해하는 것이 매우 중요합니다.
RFID 태그의 메모리 유형
- ROM(읽기 전용 메모리): 제조 과정에서 기록된 데이터입니다. 변경할 수 없습니다.
- EEPROM(전기적으로 지워지는): 재기록 가능; 현대식 RFID에서 가장 흔히 사용됨.
- RAM: 임시 저장소로, 주로 활성 트랜잭션 중에 사용됩니다.
일반적인 메모리 유형
- 읽기 전용(RO): 변경할 수 없습니다. 고정 ID에 사용됩니다.
- 읽기/쓰기(RW): 호환 가능한 리더기로 수정 가능.
- WORM(Write Once, Read Many): 한 번 기록된 데이터는 잠금 처리됩니다.
EPCglobal Gen2 태그(UHF)의 메모리 뱅크
| 메모리 뱅크 | 목차 | 쓰기 가능? |
|---|---|---|
| (주)에프씨씨 | 제품 ID (일반적으로 96~128비트) | ✅ |
| TID | 고유 태그/칩 식별자 | ❌ |
| 사용자 메모리 | 응용 프로그램별 데이터 | ✅ |
| 예약됨 | 접근/종료 명령어용 비밀번호 | ✅ (제한됨) |
모범 사례: SKU 또는 제품 식별자에는 EPC를 사용하고, 타임스탬프, 로트 번호 또는 물류 메타데이터와 같은 추가 데이터에는 사용자 메모리를 사용하십시오.
비트 및 블록 포맷팅
- 메모리는 블록(16비트 또는 32비트)으로 나뉩니다.
- 각 블록은 개별적으로 주소를 지정할 수 있습니다.
- 데이터 인코딩은 블록 크기와 태그 사양을 준수해야 합니다.
예시: 512비트의 사용자 메모리를 가진 태그는 인코딩에 사용할 수 있는 64바이트를 보유합니다 – 이에 맞춰 데이터 구조를 계획하십시오.
RFID 태그의 데이터는 얼마나 안전한가?
RFID 기술이 공급망과 소비자 제품에 더욱 통합됨에 따라 데이터 보안은 최우선 관심사가 되었습니다. RFID 태그가 데이터를 보호하는 방식과 때로는 노출시키는 방식을 이해하는 것은 안전한 배포를 위해 매우 중요합니다.
RFID 태그는 해킹될 수 있을까?
그렇습니다 — 하지만 맥락이 중요합니다. 기본적인 저가형 태그는 복제되거나 스키밍될 수 있지만, 대부분의 현대식 RFID 시스템은 접근 제어 및 암호화를 포함한 다중 보안 계층을 구현합니다.
RFID 태그의 보안 메커니즘
| 보안 기능 | 설명 | 보호 수준 |
|---|---|---|
| 비밀번호 보호 | 무단 읽기/쓰기를 차단합니다 | 중간 |
| 액세스 제어 비트 | 메모리 뱅크별로 읽기/쓰기 권한 정의 | 높은 |
| 암호화 (AES, DES) | 고보안 태그(예: 은행, 출입 통제)에 사용됨 | 매우 높음 |
| 킬 명령어 | 태그를 영구적으로 비활성화하여 오용을 방지합니다 | 문맥적 |
일반적인 취약점
- 도청: 공격자가 태그 리더기 통신을 가로챈다.
- 복제: 태그 데이터를 다른 태그에 복사하는 것.
- 재전송 공격: 포착된 전송 데이터를 재사용하는 것.
안전한 RFID 배포를 위한 모범 사례
- 중요한 데이터에는 암호로 보호되거나 암호화된 태그를 사용하십시오.
- 태그에 민감한 정보를 직접 저장하지 마십시오 — 참조나 ID만 저장하십시오.
- 태그 데이터를 검증하기 위해 안전한 백엔드 데이터베이스를 구현하십시오.
- 민감한 상황에서 사용 후 태그를 보호하거나 비활성화하십시오.
RFID 태그는 얼마나 많은 데이터를 저장할 수 있나요?
엔지니어들이 가장 자주 묻는 질문 중 하나는:
“RFID 태그에 얼마나 많은 데이터를 저장할 수 있나요?”
일반적인 RFID 메모리 용량
| 태그 유형 | 메모리 범위 | 사용 사례 |
|---|---|---|
| 저주파(LF) | 64–256 비트 | 동물 식별표, 출입 카드 |
| 고주파(HF/NFC) | 128–4,096 비트 | 스마트 카드, 재고 |
| 초고주파(UHF) | 96–8,192 비트 | 물류, 산업 추적 |
| 능동 RFID | 32KB 이상 | 센서 데이터, 대용량 페이로드 |
용량에 영향을 미치는 요소들
- 태그 빈도 & 칩 모델.
- 암호화 또는 체크섬 데이터의 사용.
- 응용 프로그램 유형 (예: EPC 인코딩 대 사용자 정의).
일반적으로 어떤 유형의 데이터가 저장되나요?
- 제품 식별자(EPC)
- 배치 번호 또는 로트 번호
- 타임스탬프
- 활성 태그의 센서 데이터(온도, 압력)
팁: 태그에는 최소한의 필수 데이터만 저장하고 세부 정보는 외부 데이터베이스에 연결하세요. 이렇게 하면 메모리 요구량을 줄이고 성능을 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
수동형 대 능동형 RFID: 데이터 저장 능력 비교
수동형과 능동형 RFID 중 선택하는 것은 비용, 데이터 용량 및 범위에 영향을 미칩니다.
| 특징 | 수동 RFID | 능동 RFID |
|---|---|---|
| 전원 | 리더로 구동됩니다 | 내장 배터리 |
| 데이터 용량 | 96–8,192 비트 | 32KB 이상 |
| 범위 | 최대 10m | 최대 100m |
| 수명 | 무제한 (배터리 없음) | 배터리 수명에 제한됨 |
| 비용 | <$0.10 per tag | 태그당 $10–$50 |
어느 쪽을 선택해야 할까요?
- 수동 태그: 재고 관리, 소매점, 출입 통제에 이상적입니다.
- 액티브 태그: 실시간 자산 추적, 물류, IoT 센서에 최적.
실제 사례 — RFID 태그에는 어떤 데이터가 저장되나요?
실제 산업 분야에서 RFID 데이터 저장 방식이 어떻게 작동하는지 살펴보겠습니다.
소매업에서
- 제품 식별 번호 (EPC)
- 가격, SKU 및 로트 번호
- 선반 위치 또는 카테고리 데이터
의료 분야에서
- 환자 ID
- 약물 용량 정보
- 장비 추적
물류 분야에서
- 발송 ID, 타임스탬프
- 컨테이너 코드
- 경로 및 체크포인트 추적
동물 추적
- 품종 ID, 백신 기록
- GPS 또는 위치 식별자(활성 태그 내)
전문가 인사이트: 대부분의 기업 시스템은 태그 ID를 클라우드 데이터베이스(ERP, WMS)에 연결하여 태그 자체에 대용량 데이터셋을 저장할 필요성을 줄입니다.
RFID 태그에 데이터가 기록되는 방식 (인코딩 과정)
하드웨어 요구 사항
- RFID 기록기 또는 읽기/기록 모듈
- 호환 소프트웨어 (TagWriter, Arduino IDE 또는 SDK)
- RFID 호환 태그
일반적인 인코딩 작업 흐름
- 작성기를 시스템 또는 마이크로컨트롤러에 연결하십시오.
- 태그 유형 및 주파수(LF, HF, UHF)를 선택하십시오.
- 데이터 형식 선택(EPC, HEX 또는 ASCII).
- 소프트웨어 명령어를 사용하여 태그에 데이터를 기록합니다.
- 읽기 함수를 사용하여 데이터를 검증하십시오.
일반적인 인코딩 형식
| 체재 | 예 | 사용 사례 |
|---|---|---|
| EPC (96비트) | 300833B2DDD9014000000001 | 제품 ID |
| HEX | 0xA1B2C3D4 | 이진 데이터 저장 |
| ASCII | “ITEM00123” | 읽을 수 있는 문자열 |
산업용 인코더가 필요하신가요? 저희 제품을 둘러보세요. RFID 라이터 키트 UHF 및 NFC 시스템용.
RFID vs. 바코드 vs. NFC: 데이터 저장 비교
| 특징 | 무선 주파수 식별(RFID) | 바코드 | 근거리 무선 통신 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 데이터 용량 | 64비트–32KB | 12–20자 | 최대 4KB |
| 읽기 범위 | 1–100 m | 0.2–1 m | 0-10cm |
| 재작성 가능? | 예 | 아니요 | 예 |
| 동시 읽기 | 수백 개의 태그 | 한 번에 하나씩 | 한 번에 하나씩 |
| 내구성 | 높은 | 낮은 | 중간 |
주요 요점
- RFID: 고속, 대용량 데이터 환경에 최적입니다.
- 바코드: 정적 ID에 간단하고 저렴합니다.
- NFC: 보안이 강화된 근거리 상호작용(예: 결제)에 이상적입니다.
바코드에서 RFID로 업그레이드할 계획이 있으신가요? 무료 구현 견적을 받아보세요.
RFID 데이터 저장에 관한 자주 묻는 질문
RFID 태그는 재기록이 가능한가요?
예 — 대부분의 HF 및 UHF 태그는 메모리 마모가 발생할 때까지 여러 번의 쓰기 주기를 지원합니다.
RFID 태그에 데이터는 얼마나 오래 남아 있나요?
수동 태그의 경우 칩 품질에 따라 최대 10년 이상 지속됩니다.
RFID 데이터는 암호화되어 있습니까?
일부 태그는 AES/DES 암호화를 지원하며, 다른 태그는 암호 보호에 의존합니다.
스마트폰으로 RFID 태그를 프로그래밍할 수 있나요?
네, 해당 기기가 NFC 호환(13.56 MHz)이고 휴대폰에 NFC 리더기가 장착되어 있다면 가능합니다.
RFID 태그에 데이터를 기록하는 데 어떤 소프트웨어가 사용됩니까?
TagWriter, Arduino IDE(라이브러리 포함), 또는 제조업체 SDK.
RFID 데이터 저장 기술의 미래
RFID의 미래는 IoT와 AI의 교차점에 있다. 여기서 태그는 단순히 데이터를 저장하는 것을 넘어 클라우드 시스템 및 센서와 능동적으로 통신한다.
신흥 혁신
- 마이크로 EEPROM 기술을 통한 메모리 밀도 향상
- 온도 또는 동작 데이터를 저장하는 통합 센서
- 인공지능 기반 RFID 분석을 통한 의사 결정 자동화
- 블록체인 기반 제품 진위성 추적성
결론: 종합해 보면
RFID 태그는 작지만 강력한 데이터 저장 장치로, 현대 자동화의 기반을 이룹니다.
기본 메모리 구조부터 고급 암호화에 이르기까지, RFID 태그가 데이터를 저장하고 전송하는 방식을 이해하면 엔지니어, 개발자 및 기업이 더 스마트하고 안전한 시스템을 구축할 수 있습니다.
주요 내용:
- 범위, 용량 및 적용 분야에 따라 태그 유형을 선택하십시오.
- 민감한 데이터에는 안전한 암호화 방식을 사용하십시오.
- 확장성을 위해 RFID를 백엔드 시스템과 통합하십시오.
RFID 시스템 설계나 프로그래밍에 도움이 필요하신가요?
팀에 문의 맞춤형 RFID 솔루션, 하드웨어 조달 및 구현 지원을 위해.

레이 저우
이 글은 업계에서 10년 이상의 경력을 쌓은 RFID 기술 전문가인 Ray Zhou가 작성했습니다.
댓글
인기상품

13.56MHz RFID 카드 및 태그 설명: 알아야 할 모든 것
RFID 기술은 최신 식별 및 데이터 교환 시스템에서 중요한 역할을 합니다. 다양한 RFID 주파수 중 13.56MHz

물류에서의 RFID: RFID 오경로 및 RFID 라벨 오류를 제거하는 방법
물류 분야의 RFID는 단순히 프로세스 가속화를 위한 도구를 넘어, 현대 공급망 운영 방식의 핵심 요소로 자리매김했습니다.

RFID 기반 폐기물 관리란 무엇인가
모든 쓰레기통이 말을 하는 도시를 상상해 보세요. 말 그대로가 아니라, 작은 칩을 통해 시스템에 쓰레기통이 가득 찼을 때, 비워졌을 때, 그리고 어디로 이동했는지를 알려주는 것입니다. 이것이 바로 오늘날 RFID 폐기물 관리가 수행하는 역할입니다.

볼트 씰이란 무엇이며 어떤 용도로 사용되나요? | 전체 가이드
글로벌 무역 및 물류에서 볼트 씰은 화물의 보안과 규정 준수에 중요한 역할을 합니다. 이 작지만 강력한 장치는 운송 컨테이너, 트레일러 및 화물 도어를 변조 방지 메커니즘으로 잠그도록 설계되었습니다.

RFID 카드 프로텍터란 무엇인가요? 장점, 사용 사례 및 구매 가이드
RFID(무선 주파수 식별) 기술은 신용카드, 신분증, 대중교통 패스, 호텔 객실 열쇠 등 어디에나 있습니다. 이 기술은 속도와 편리함을 제공하지만 "스키밍"이라는 새로운 종류의 디지털 도난에 대한 문을 열어주기도 합니다. 이것이 바로 RFID 카드 프로텍터가 필요한 이유입니다.

이벤트용 RFID 손목 밴드: 주최자를 위한 대량 구매 가이드
이벤트용 RFID 손목 밴드는 콘서트, 축제, 스포츠 경기장에서 더 빠른 입장, 사기 방지, 현금 없는 결제가 필요한 주최자가 선호하는 솔루션으로 자리 잡고 있습니다. 종이 티켓이나 QR코드와 달리 이러한 스마트 손목 밴드는 내장된 칩을 사용하여 액세스를 간소화하고 거래를 보호하며 게스트 경험을 개선합니다.
태그
관련 블로그

13.56MHz RFID 카드 및 태그 설명: 알아야 할 모든 것
RFID 기술은 최신 식별 및 데이터 교환 시스템에서 중요한 역할을 합니다. 다양한 RFID 주파수 중 13.56MHz

물류에서의 RFID: RFID 오경로 및 RFID 라벨 오류를 제거하는 방법
물류 분야의 RFID는 단순히 프로세스 가속화를 위한 도구를 넘어, 현대 공급망 운영 방식의 핵심 요소로 자리매김했습니다.

RFID 기반 폐기물 관리란 무엇인가
모든 쓰레기통이 말을 하는 도시를 상상해 보세요. 말 그대로가 아니라, 작은 칩을 통해 시스템에 쓰레기통이 가득 찼을 때, 비워졌을 때, 그리고 어디로 이동했는지를 알려주는 것입니다. 이것이 바로 오늘날 RFID 폐기물 관리가 수행하는 역할입니다.




