
An In-Depth Analysis of RFID Adhesive Tags
Table of Contents
Summary
These tags are designed to facilitate the tracking and management of objects through electromagnetic waves, leveraging their adhesive properties for versatile applications. This article provides a comprehensive examination of RFID adhesive tags, including their types, functionalities, and practical applications.
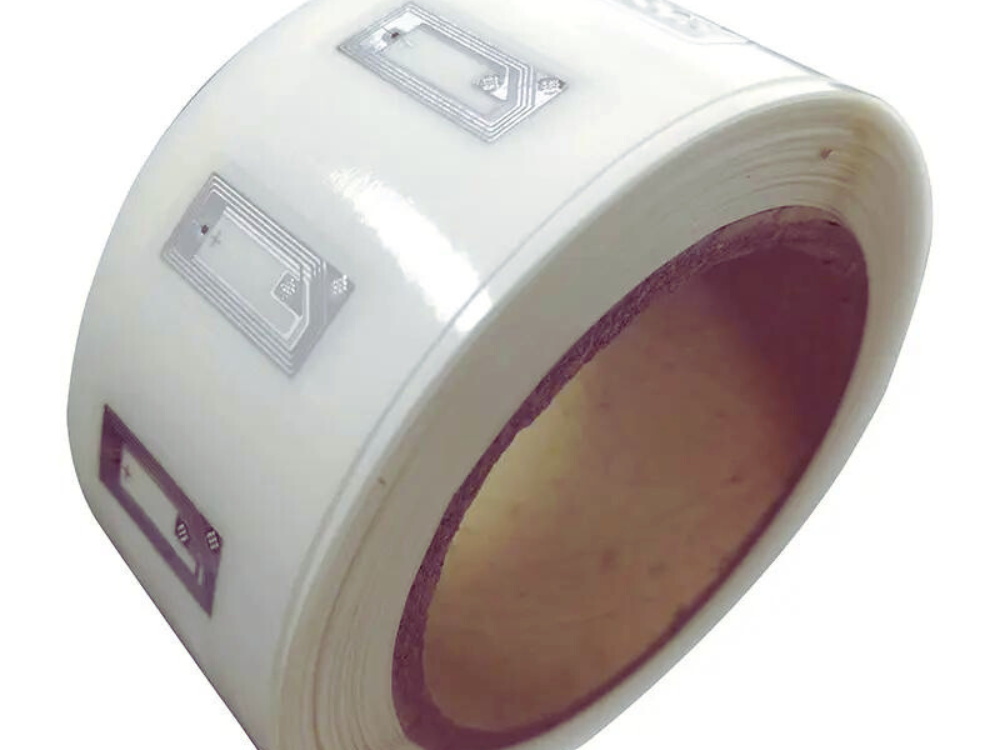

Understanding RFID Adhesive Tags
RFID adhesive tags are small, self-adhesive devices with an integrated circuit and an antenna. These tags can be affixed to various surfaces, enabling the transmission and reception of data through radio frequency signals. They come in various forms and can be tailored to meet specific needs in diverse environments. The adhesive backing allows these tags to be easily applied to products, assets, and packaging, making them highly adaptable for numerous tracking and identification purposes.
Components of RFID Adhesive Tags
To comprehend the functionality of RFID adhesive tags, it’s essential to understand their core components:
- Integrated Circuit (IC): This microchip stores the tag’s unique identifier and any additional data. It processes the signals received from the RFID reader and responds accordingly.
- Antenna: The antenna transmits and receives radio waves to and from the RFID reader. Its design influences the tag’s communication range and effectiveness.
- Adhesive Layer: The adhesive backing allows the tag to be securely attached to various surfaces, ensuring stability and durability in different conditions.
Types of RFID Adhesive Tags
RFID adhesive tags come in several types, each suited for different applications. The following table outlines the primary categories:
Type | Description | Typical Applications |
Passive Tags | Operate without a battery; powered by the reader’s signal. | Inventory management, asset tracking, logistics. |
Active Tags | Equipped with a battery to power the tag and extend its range. | High-value asset tracking, real-time location systems. |
Semi-Passive Tags | Combine a battery with passive technology; battery powers the chip but not the transmission. | Environmental monitoring, sensitive equipment tracking. |
Custom Tags | Tailored to specific needs or environments; may include specialized adhesives or form factors. | Specialized industries, customized product labeling. |
Passive RFID Adhesive Tags
Passive RFID adhesive tags do not have an internal power source. Instead, they rely on the energy emitted by the RFID reader to power the tag’s integrated circuit. This type of tag is cost-effective and widely used in inventory management and asset tracking.
Active RFID Adhesive Tags
Active RFID adhesive tags contain an internal battery that powers both the chip and the transmission of data. This allows for greater range and more frequent updates, making them ideal for high-value asset tracking and real-time location systems.
Semi-Passive RFID Adhesive Tags
Semi-passive RFID adhesive tags use a battery to power the tag’s integrated circuit but rely on the reader’s signal for data transmission. These tags offer enhanced performance compared to passive tags and are used in environmental monitoring and sensitive equipment tracking.
Custom RFID Adhesive Tags
Custom RFID adhesive tags are designed to meet specific requirements or to function in specialized environments. They may feature unique adhesives, sizes, or shapes to accommodate various applications, such as specialized product labeling or harsh environmental conditions.
Applications of RFID Adhesive Tags
RFID adhesive tags are versatile and can be used in numerous fields. Here are some key applications:
Inventory and Supply Chain Management
RFID adhesive tags enhance inventory accuracy and efficiency by enabling real-time tracking of goods throughout the supply chain. Their ability to be easily attached to products and packaging makes them ideal for managing stock levels, reducing losses, and improving logistics.
Asset Tracking
In asset tracking, RFID adhesive tags help monitor the location and status of valuable assets. Their adhesive properties allow them to be securely affixed to equipment, tools, and other assets, facilitating effective management and reducing the risk of loss.
Retail and Consumer Goods
In retail, RFID adhesive tags are used for automated checkout processes, anti-theft measures, and inventory management. Their ease of application to products and packaging makes them a valuable tool for enhancing the shopping experience and streamlining store operations.
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
RFID adhesive tags play a crucial role in healthcare by tracking medical equipment, medications, and patient information. Their use helps ensure accurate administration of drugs, proper management of medical assets, and improved patient safety.
Environmental Monitoring
In environmental monitoring, RFID adhesive tags are used to track conditions such as temperature and humidity. Their semi-passive or active variants can provide real-time data, making them suitable for monitoring sensitive environments or products.
Selecting RFID Adhesive Tags
When choosing RFID adhesive tags, consider the following factors:
Application Requirements
Identify the specific needs of your application, including the type of environment, the required range, and the nature of the items being tagged. This will help determine whether passive, active, or semi-passive tags are most suitable.
Adhesive Properties
Evaluate the adhesive properties of the tag, such as its strength, durability, and suitability for various surfaces. Ensure the adhesive will maintain its bond in the intended application environment.
Performance Specifications
Assess the tag’s performance characteristics, including read range, data capacity, and communication speed. These factors will influence the efficiency and effectiveness of the RFID system.
Cost Considerations
Consider the cost of the tags in relation to their performance and application needs. Factor in not only the initial purchase cost but also any potential long-term costs associated with maintenance or replacement.
Conclusion
RFID adhesive tags represent a significant technological advancement in tracking and identification. Their diverse types and applications make them suitable for a wide range of industries, from retail to healthcare. By understanding the different types of RFID adhesive tags and their respective applications, businesses can leverage this technology to enhance operational efficiency and data accuracy.
Comments
Hot Products

RFID in Logistics: How to Eliminate RFID Misrouting and RFID Label Failures
RFID in logistics is more than just a tool to speed up processes. It has become a key part of how modern supply chains operate.

What Is RFID Waste Management
Imagine a city where every trash bin speaks — not literally — but through a tiny chip that tells the system when it’s full, when it’s emptied, and where it went. That’s what RFID waste management is doing today.

What are Bolt Seals and their Applications? | Complete Guide
In global trade and logistics, bolt seals play a crucial role in ensuring cargo security and compliance. These small but powerful devices are designed to lock shipping containers, trailers, and cargo doors with a tamper-evident mechanism.

What is an RFID Card Protector? Benefits, Use Cases, and Buying Guide
RFID technology (Radio Frequency Identification) is everywhere: in your credit cards, ID badges, transit passes, hotel room keys, and more. It offers speed and convenience, but it also opens the door to a new kind of digital theft called “skimming.” That’s where an RFID card protector comes in.

RFID Wristbands for Events: Bulk Buying Guide for Organizers
RFID wristbands for events are becoming the go-to solution for organizers who need faster entry, fraud prevention, and cashless payments at concerts, festivals, and sports venues. Unlike paper tickets or QR codes, these smart wristbands use embedded chips to streamline access, secure transactions, and improve the guest experience.

How RFID Tag on Windscreen Improves Vehicle Access Control and Toll Systems
In today’s fast-paced world, vehicle identification needs to be quick, secure, and contactless. An RFID Tag on the Windscreen provides exactly that — a reliable way to manage toll collection, parking, and gated access without stopping vehicles.
Tags
RELATED BLOGS

RFID in Logistics: How to Eliminate RFID Misrouting and RFID Label Failures
RFID in logistics is more than just a tool to speed up processes. It has become a key part of how modern supply chains operate.

What Is RFID Waste Management
Imagine a city where every trash bin speaks — not literally — but through a tiny chip that tells the system when it’s full, when it’s emptied, and where it went. That’s what RFID waste management is doing today.

What are Bolt Seals and their Applications? | Complete Guide
In global trade and logistics, bolt seals play a crucial role in ensuring cargo security and compliance. These small but powerful devices are designed to lock shipping containers, trailers, and cargo doors with a tamper-evident mechanism.




