
What are the Challenges and Limitations of RFID Technology?
How RFID Library Tags Are Revolutionizing Library Management?
Table of Contents
Introduction to RFID Library Tags
This article will explore how RFID Library tags work in libraries, their benefits, and why they’re becoming an essential tool for modern, smart libraries. Whether you’re a librarian, a tech enthusiast, or simply curious about the future of libraries, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights into the world of RFID in library management.
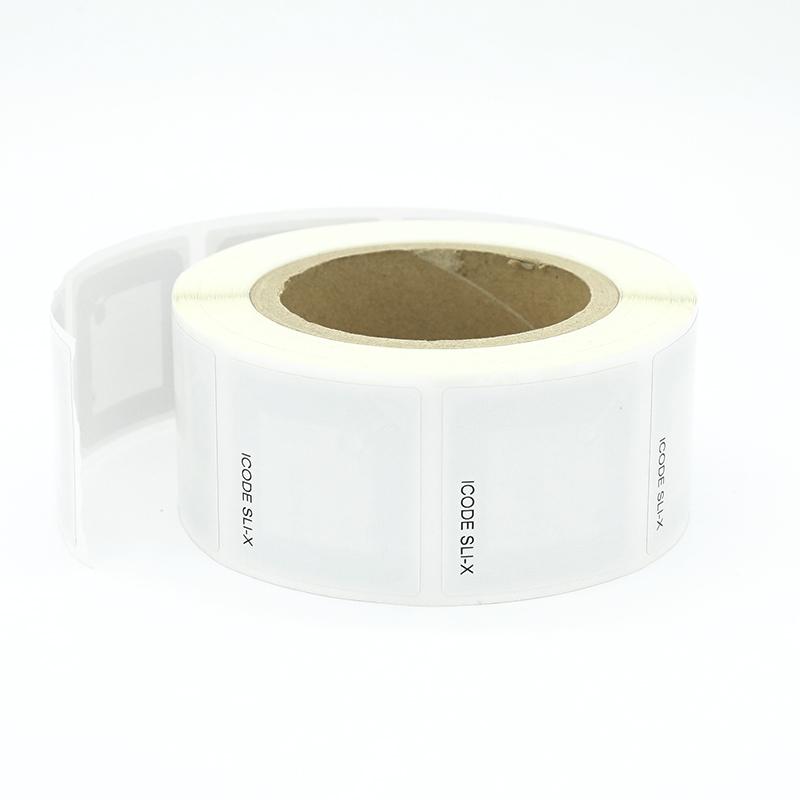

What Are RFID Library Tags and How Do They Work in Libraries?
RFID Library tags are small electronic devices that use radio waves to communicate information. In libraries, these tags are typically placed on books, DVDs, and other items in the collection. Each RFID Library tag contains a unique identifier and can store additional information about the item. Here’s how RFID works in a library setting:
- Tag Placement: An RFID Library tag is attached to each library item, usually on the inside cover of books or on the surface of other materials.
- Data Storage: The tag stores information such as the item’s ID number, title, and checkout status.
- Reader Interaction: When an item passes through an RFID reader, the tag’s information is captured without direct line-of-sight.
- Database Update: The library’s management system instantly updates the item’s status in the database.
This technology allows for faster check-ins and check-outs, improved inventory management, and enhanced security features.
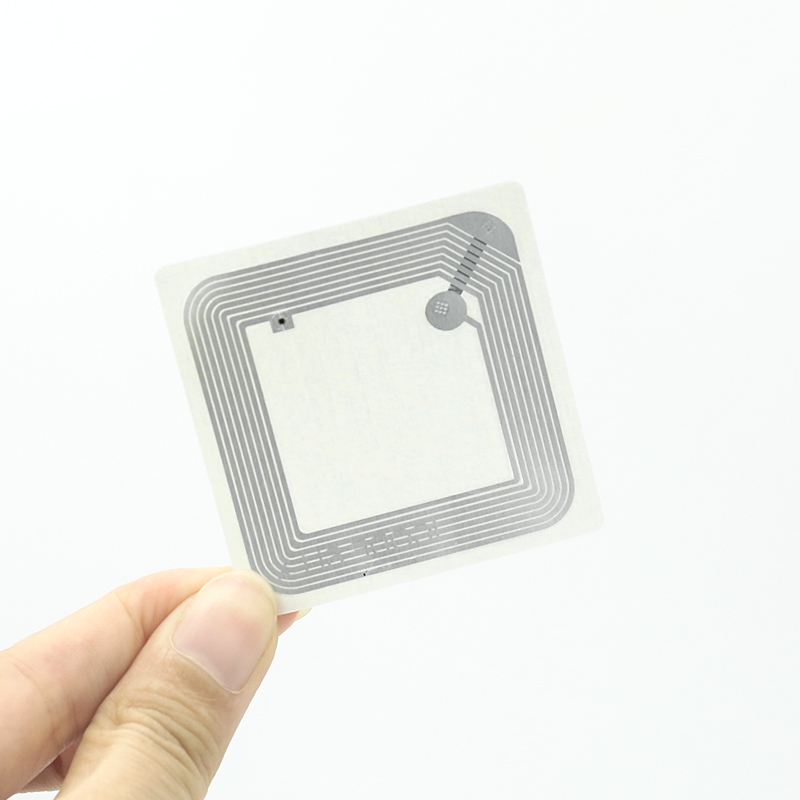

How Do RFID Library Tags Differ from Traditional Barcodes?
While barcodes have been a staple in libraries for decades, RFID Library tags offer several advantages:
- Multiple Item Scanning: RFID readers can scan multiple items simultaneously, unlike barcodes which require individual scanning.
- No Line-of-Sight Required: RFID book tags can be read even when not directly visible to the scanner.
- More Data Storage: RFID book tags can store more information than a barcode, including checkout history and security status.
- Durability: RFID Library tags are more durable and less prone to damage than printed barcodes.
- Updated Information: Unlike static barcodes, RFID Library tags can be updated with new information as needed.
These differences make RFID a more efficient and versatile option for modern library management.
What Are the Key Benefits of Using RFID in Libraries?
Implementing RFID technology in libraries offers numerous advantages:
- Faster Check-In/Check-Out: Patrons can check out multiple items at once, reducing wait times.
- Improved Inventory Management: Libraries can conduct faster and more accurate inventory checks.
- Enhanced Security: RFID gates at exits can detect unauthorized item removal.
- Self-Service Options: Patrons can use self-checkout kiosks, freeing up staff for other tasks.
- Automated Sorting: RFID-enabled sorting systems can quickly organize returned items.
- Data Analytics: Libraries can gather more detailed usage data to inform collection development.
These benefits contribute to a more efficient library operation and an improved user experience.
How Are RFID Library Tags Placed on Library Items?
The placement of RFID Library tags on library items is crucial for optimal performance. Here are some best practices:
- Books: Tags are typically placed on the inside cover, away from the spine to avoid interference from metal shelving.
- DVDs and CDs: Tags are usually placed on the surface of the disc or inside the case.
- Magazines: Tags can be placed inside the cover or on a special page designated for library use.
Proper placement ensures consistent reading by RFID scanners and helps maintain the integrity of the library materials.
What Equipment Is Needed for an RFID Library System?
To implement an RFID system in a library, several key components are required:
- RFID Library Tags: The tags that are attached to library items.
- RFID Readers: Devices that scan and read the information from the tags.
- Security Gates: RFID-enabled gates at library exits to prevent theft.
- Self-Checkout Kiosks: Stations where patrons can check out items independently.
- Staff Workstations: Equipped with RFID readers for processing items.
- Handheld Readers: Portable devices for inventory and shelf reading.
- Software: Library management system that integrates with RFID technology.
This equipment works together to create a comprehensive RFID-based library management solution.
How Does RFID Improve Library Security?
RFID technology enhances library security in several ways:
- Theft Detection: RFID gates at exits can detect items that haven’t been properly checked out.
- Item Tracking: The system can locate misplaced items within the library.
- Inventory Control: Regular RFID scans can quickly identify missing items.
- Access Control: RFID-enabled library cards can manage patron access to restricted areas.
These security features help protect the library’s collection and ensure that resources are available when patrons need them.
What Challenges Might Libraries Face When Implementing RFID?
While RFID offers many benefits, there are some challenges to consider:
- Initial Cost: The upfront investment for RFID equipment and tags can be significant.
- Staff Training: Employees need to learn new systems and procedures.
- Privacy Concerns: Some patrons may worry about the tracking capabilities of RFID.
- Technical Issues: Like any technology, RFID systems can experience glitches or downtime.
- Tag Interference: Metal objects or closely stacked items can sometimes interfere with RFID signals.
Libraries should carefully plan their RFID implementation to address these potential challenges.

How Can Libraries Maximize the Benefits of RFID Technology?
To get the most out of RFID technology, libraries can:
- Integrate with Existing Systems: Ensure RFID works seamlessly with current library management software.
- Train Staff Thoroughly: Provide comprehensive training on RFID equipment and procedures.
- Educate Patrons: Offer guidance on using self-checkout kiosks and other RFID features.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep RFID equipment in good working order through routine checks.
- Utilize Data: Analyze RFID-generated data to inform collection development and space usage.
- Expand Services: Explore innovative uses of RFID, such as after-hours book lockers or automated returns.
By taking these steps, libraries can fully leverage the potential of RFID technology.
What Does the Future Hold for RFID in Libraries?
The future of RFID in libraries looks promising, with several exciting developments on the horizon:
- Integration with IoT: RFID library tags could interact with other smart devices in the library.
- Enhanced User Experience: Personalized recommendations based on checkout history.
- Improved Analytics: More sophisticated data analysis for better resource allocation.
- Contactless Services: Expanded touchless options for borrowing and returning items.
Smart Shelves: Shelves that can track item locations and alert staff to misplaced books.
As technology continues to evolve, RFID is likely to play an increasingly important role in creating smart, efficient libraries. In conclusion, RFID Library tags are transforming library management, offering a range of benefits from improved efficiency to enhanced security. As libraries continue to adapt to the digital age, RFID technology provides a powerful tool for streamlining operations and improving the patron experience. While challenges exist, the potential advantages make RFID an attractive option for libraries looking to modernize their services and stay relevant in an increasingly tech-savvy world.
Comments
Hot Products

RFID in Logistics: How to Eliminate RFID Misrouting and RFID Label Failures
RFID in logistics is more than just a tool to speed up processes. It has become a key part of how modern supply chains operate.

What Is RFID Waste Management
Imagine a city where every trash bin speaks — not literally — but through a tiny chip that tells the system when it’s full, when it’s emptied, and where it went. That’s what RFID waste management is doing today.

What are Bolt Seals and their Applications? | Complete Guide
In global trade and logistics, bolt seals play a crucial role in ensuring cargo security and compliance. These small but powerful devices are designed to lock shipping containers, trailers, and cargo doors with a tamper-evident mechanism.

What is an RFID Card Protector? Benefits, Use Cases, and Buying Guide
RFID technology (Radio Frequency Identification) is everywhere: in your credit cards, ID badges, transit passes, hotel room keys, and more. It offers speed and convenience, but it also opens the door to a new kind of digital theft called “skimming.” That’s where an RFID card protector comes in.

RFID Wristbands for Events: Bulk Buying Guide for Organizers
RFID wristbands for events are becoming the go-to solution for organizers who need faster entry, fraud prevention, and cashless payments at concerts, festivals, and sports venues. Unlike paper tickets or QR codes, these smart wristbands use embedded chips to streamline access, secure transactions, and improve the guest experience.

How RFID Tag on Windscreen Improves Vehicle Access Control and Toll Systems
In today’s fast-paced world, vehicle identification needs to be quick, secure, and contactless. An RFID Tag on the Windscreen provides exactly that — a reliable way to manage toll collection, parking, and gated access without stopping vehicles.
Tags
RELATED BLOGS

RFID in Logistics: How to Eliminate RFID Misrouting and RFID Label Failures
RFID in logistics is more than just a tool to speed up processes. It has become a key part of how modern supply chains operate.

What Is RFID Waste Management
Imagine a city where every trash bin speaks — not literally — but through a tiny chip that tells the system when it’s full, when it’s emptied, and where it went. That’s what RFID waste management is doing today.

What are Bolt Seals and their Applications? | Complete Guide
In global trade and logistics, bolt seals play a crucial role in ensuring cargo security and compliance. These small but powerful devices are designed to lock shipping containers, trailers, and cargo doors with a tamper-evident mechanism.




