
How Do RFID Tags Work?
Table of Contents
A Complete Beginner’s Guide to Passive & Active RFID Systems
But how exactly do RFID tags work — and which type is right for your application?
In this guide, we’ll explain how RFID tags function, the types available, and their use in logistics, retail, healthcare, and manufacturing.
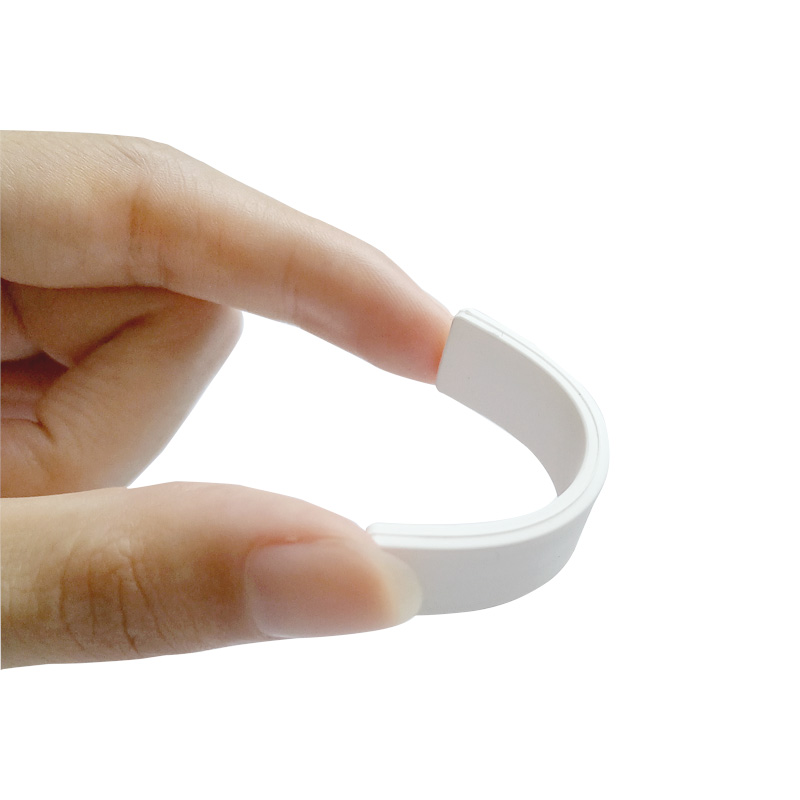

What Is an RFID Tag?
An RFID tag is a small device that stores data and communicates wirelessly with an RFID reader. Tags can be embedded into objects, worn as wristbands, or attached to assets using adhesive, screws, or ties.
Every RFID tag contains two essential components:
Microchip – stores a unique ID and sometimes user-defined data
Antenna – transmits and receives signals to/from a reader
Some tags also contain a battery (for active tags) to boost range and signal strength.
How Do RFID Systems Work?
An RFID system typically includes three main components:
1. RFID Tag – Attached to the item or asset
2. RFID Reader – Sends a signal and receives data from tags
3. Backend System (Software/Database) – Stores and processes the tag data.
The Process:
- The reader emits radio waves.
- The tag receives the signal and sends back its stored data.
- The backend system logs, processes, or automates actions based on that data.
This entire interaction can happen in real-time, without physical contact.
Types of RFID Tags
There are three main types of RFID tags, each with unique capabilities:
Passive RFID Tags
Power Source: No battery (powered by the reader signal)
Read Range: Up to 12 meters (typically less)
Lifespan: 10+ years
Cost: Low
Best For:
- Retail inventory
- Library book tracking
- Supply chain logistics
- Smart shelves and anti-theft systems
Passive RFID is the most commonly used type. It is durable, cost-effective, and reliable for short—to mid-range scanning.
Active RFID Tags
Power Source: Internal battery
Read Range: 30–100 meters or more
Lifespan: 3–5 years (battery dependent)
Cost: Higher
Best For:
- Vehicle and fleet tracking
Real-time location systems (RTLS) - Construction and mining safety
- Cold chain logistics
Active tags constantly broadcast signals and are ideal for real-time, long-range tracking in large environments.
Semi-Passive (Battery-Assisted) RFID Tags
- Powered by a battery but only activates when triggered by a reader
- Greater reliability in difficult environments (metal, liquids)
- Balances range and battery life
Semi-passive tags are used in harsh industrial or medical environments where passive tags may fail.

What Are RFID Tags Used For?
RFID tags are used in dozens of industries to increase efficiency, visibility, and control.
Logistics & Supply Chain
- Track goods throughout warehouses and delivery
- Automate receiving and dispatch processes
Retail & Inventory
- Real-time stock visibility
- Reduce shrinkage and stockouts
Healthcare
- Track medical equipment and supplies
- Patient safety (ID wristbands, medication matching)
Manufacturing
- Tracked parts through production lines.
- Ensure quality control and traceability
Understanding RFID Tag Range
Several factors impact how far a tag can communicate:
| Factor | Effect |
|---|---|
| Tag type | Active tags have longer range |
| Frequency band | UHF > HF > LF (in range) |
| Environment | Metal/liquid can interfere |
| Reader placement | Affects scan efficiency |
Tip: Use on-metal RFID tags for challenging environments like manufacturing.
How to Attach RFID Tags Correctly
Improper placement can affect readability. Here’s what to consider:
Avoid metal/liquid unless using specialized tags
Place in an exposed, accessible location
Use adhesive, screws, or zip ties based on environment
RFID Tags and Smart Labels: What's the Difference?
RFID tags and smart labels are often confused, but they serve different purposes:
RFID Tags: Typically more durable and versatile, RFID tags are used in a wide range of applications where long-term tracking and identification are required.
Smart Labels: These are essentially RFID tags embedded within a traditional printed label. Smart labels are more flexible and can be printed on demand, making them ideal for inventory management and retail applications.
Choosing between RFID tags and smart labels depends on the specific needs of the application, including durability, cost, and required features.
The Future of RFID Technology: Trends and Innovations
RFID technology continues to evolve, with several exciting trends on the horizon:
IoT Integration: RFID is becoming an integral part of the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling seamless connectivity and data exchange between physical objects and digital systems.
Smaller and More Efficient Tags: Technological advances are leading to smaller, more powerful RFID tags that can be used in more applications.
Increased Adoption: As costs continue to decrease and technology improves, more industries are adopting RFID systems to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
The future of RFID is bright, with innovations that will further enhance its capabilities and expand its applications.
Choosing the Right RFID Tag for Your Application
When selecting an RFID tag, consider the following:
- Read range needed
- Tag environment (metal, water, heat, chemicals)
- Data requirements (read-only or read/write)
- Cost per unit
- Integration with your existing system
Need help choosing? Contact us for expert advice or request a free sample kit to test in your environment.
Comments
Hot Products

13.56 MHz RFID Cards and Tags Explained: Everything You Should Know
RFID technology plays an important role in modern identification and data exchange systems. Among the different RFID frequencies, 13.56 MHz

RFID in Logistics: How to Eliminate RFID Misrouting and RFID Label Failures
RFID in logistics is more than just a tool to speed up processes. It has become a key part of how modern supply chains operate.

What Is RFID Waste Management
Imagine a city where every trash bin speaks — not literally — but through a tiny chip that tells the system when it’s full, when it’s emptied, and where it went. That’s what RFID waste management is doing today.

What are Bolt Seals and their Applications? | Complete Guide
In global trade and logistics, bolt seals play a crucial role in ensuring cargo security and compliance. These small but powerful devices are designed to lock shipping containers, trailers, and cargo doors with a tamper-evident mechanism.

What is an RFID Card Protector? Benefits, Use Cases, and Buying Guide
RFID technology (Radio Frequency Identification) is everywhere: in your credit cards, ID badges, transit passes, hotel room keys, and more. It offers speed and convenience, but it also opens the door to a new kind of digital theft called “skimming.” That’s where an RFID card protector comes in.

RFID Wristbands for Events: Bulk Buying Guide for Organizers
RFID wristbands for events are becoming the go-to solution for organizers who need faster entry, fraud prevention, and cashless payments at concerts, festivals, and sports venues. Unlike paper tickets or QR codes, these smart wristbands use embedded chips to streamline access, secure transactions, and improve the guest experience.
Tags
RELATED BLOGS

13.56 MHz RFID Cards and Tags Explained: Everything You Should Know
RFID technology plays an important role in modern identification and data exchange systems. Among the different RFID frequencies, 13.56 MHz

RFID in Logistics: How to Eliminate RFID Misrouting and RFID Label Failures
RFID in logistics is more than just a tool to speed up processes. It has become a key part of how modern supply chains operate.

What Is RFID Waste Management
Imagine a city where every trash bin speaks — not literally — but through a tiny chip that tells the system when it’s full, when it’s emptied, and where it went. That’s what RFID waste management is doing today.




