
How RFID Tags Store Data?
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding this process isn’t just academic. For engineers designing smart supply chains, developers building RFID-integrated apps, and IT managers overseeing large-scale asset tracking, the underlying mechanics of RFID memory, data encoding, and security protocols are critical for performance, interoperability, and data integrity.

What Is RFID and How Does It Work?
What Is RFID?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a wireless technology that automatically identifies and tracks objects using electromagnetic fields. Unlike barcodes, RFID doesn’t need direct line-of-sight and can store more data directly on the tag.
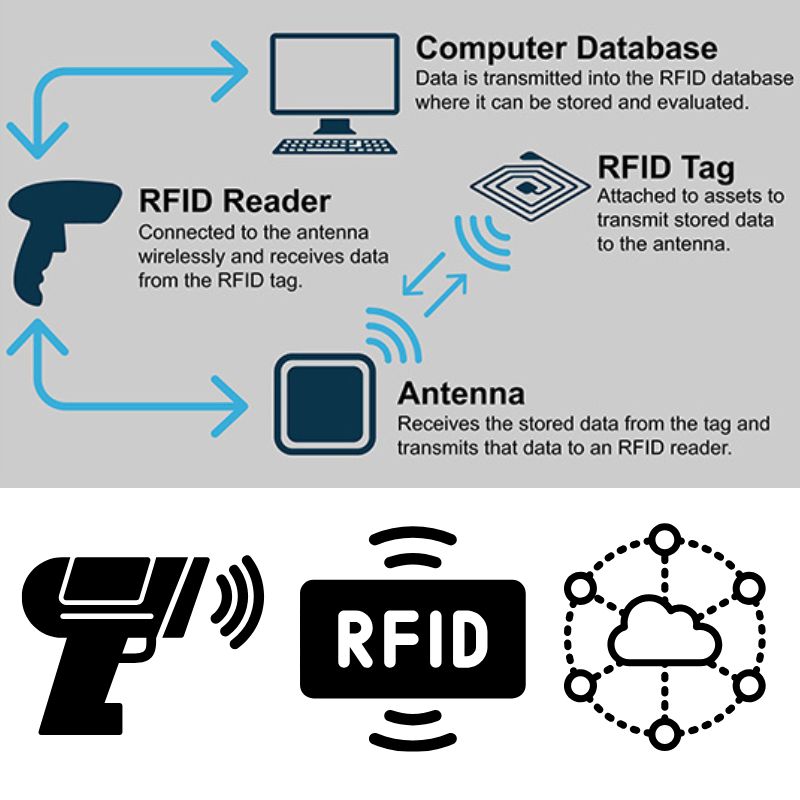
Key Components of an RFID System
- RFID Tag (Transponder): A chip and antenna embedded in a label or object that stores data.
- RFID Reader (Interrogator): Sends a radio signal to activate the tag and receive its data.
- Middleware/System Software: Processes, stores, and routes data to databases or applications.
How Data Transmission Works
When the RFID reader emits a radio frequency signal, the tag’s antenna picks it up and powers the chip (if passive). The chip then modulates and sends its stored data back to the reader. This communication varies by frequency:
- LF (Low Frequency): Short range, good for animal tracking.
- HF (High Frequency): Common in NFC and smart cards.
- UHF (Ultra High Frequency): Longer range, faster read speeds – ideal for logistics.
Engineering Tip: Passive UHF tags are most commonly used in industrial supply chains because they’re low-cost and can transmit up to several meters.
Beginner’s Guide to Programming RFID Tags
Programming RFID tags can unlock powerful capabilities — from customizing product data to enabling secure access control. While many tools and approaches are available, the specific method depends on the tag type, frequency, and application.
We are currently working on verified code examples and practical walkthroughs for programming RFID tags safely and effectively. This section will soon include:
- Hands-on tutorials for using Arduino with RFID modules.
- Encoding data using TagWriter (Android) for NFC-compatible tags.
- Using RFID SDKs and desktop writers for enterprise applications.
- Tips on selecting the right memory format (ASCII, HEX, EPC).
Want to start now? We recommend exploring these resources in the meantime:
- NXP TagWriter App– NFC encoding for Android
- MFRC522 Arduino Library on GitHub– Open-source RFID reader library
- [Your hardware vendor’s SDK or developer tools] for specific reader models
Need help writing data to your RFID tags or choosing compatible tools? Contact our technical team for personalized support.
How RFID Tags Store Data Internally
At its core, an RFID tag is a tiny storage device with specific memory banks. Understanding the internal memory layout is critical when planning what kind of data to store — and how much.
Types of Memory in RFID Tags
- ROM (Read-Only Memory): Data written during manufacturing. It can’t be changed.
- EEPROM (Electrically Erasable): Rewritable; most commonly used in modern RFID.
- RAM: Temporary storage, often used during active transactions.
Common Memory Types
- Read-Only (RO): Cannot be changed. Used for fixed IDs.
- Read/Write (RW): Can be modified with compatible readers.
- WORM (Write Once, Read Many): Once programmed, data is locked.
Memory Banks in EPCglobal Gen2 Tags (UHF)
| Memory Bank | Contents | Writable? |
|---|---|---|
| EPC | Product ID (96-128 bits typical) | ✅ |
| TID | Unique tag/chip identifier | ❌ |
| User Memory | Application-specific data | ✅ |
| Reserved | Passwords for access/kill commands | ✅ (Restricted) |
Best Practice: Use EPC for SKU or product identifiers, and User Memory for extra data like timestamps, lot numbers, or logistics metadata.
Bit & Block Formatting
- Memory is divided into blocks (16 or 32 bits).
- Each block can be addressed individually.
- Data encoding must respect block size and tag specs.
Example: A tag with 512 bits of User Memory has 64 bytes available for encoding – plan your data structure accordingly.
How Secure Is Data on RFID Tags?
As RFID technology becomes more integrated into supply chains and consumer products, data security has become a top concern. Understanding how RFID tags protect — and sometimes expose — data is crucial for secure deployments.
Can RFID Tags Be Hacked?
Yes — but context matters. While basic low-cost tags can be cloned or skimmed, most modern RFID systems implement multiple layers of security, including access control and encryption.
Security Mechanisms in RFID Tags
| Security Feature | Description | Protection Level |
|---|---|---|
| Password Protection | Blocks unauthorized reads/writes | Medium |
| Access Control Bits | Define read/write permissions per memory bank | High |
| Encryption (AES, DES) | Used in high-security tags (e.g., banking, access control) | Very High |
| Kill Commands | Permanently disable a tag to prevent misuse | Contextual |
Common Vulnerabilities
- Eavesdropping: Attackers intercept tag-reader communication.
- Cloning: Copying tag data onto another tag.
- Replay Attacks: Reusing captured transmission data.
Best Practices for Secure RFID Deployment
- Use password-protected or encrypted tags for critical data.
- Avoid storing sensitive information directly on tags — store only references or IDs.
- Implement secure backend databases to validate tag data.
- Shield or deactivate tags after usage in sensitive contexts.
How Much Data Can RFID Tags Store?
One of the most common questions engineers ask is:
“How much data can I store on an RFID tag?”
Typical RFID Memory Capacities
| Tag Type | Memory Range | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Low Frequency (LF) | 64–256 bits | Animal IDs, access cards |
| High Frequency (HF/NFC) | 128–4,096 bits | Smart cards, inventory |
| Ultra High Frequency (UHF) | 96–8,192 bits | Logistics, industrial tracking |
| Active RFID | 32 KB+ | Sensor data, large payloads |
Factors That Affect Capacity
- Tag frequency & chip model.
- Use of encryption or checksum data.
- Application type (e.g., EPC encoding vs user-defined).
What Type of Data Is Typically Stored?
- Product identifiers (EPC)
- Batch or lot numbers
- Timestamps
- Sensor data (temperature, pressure) in active tags
Tip: Store only the minimal data necessary on the tag and link to external databases for details. This reduces memory requirements and improves performance.
Passive vs. Active RFID: Data Storage Capabilities Compared
Choosing between passive and active RFID affects cost, data capacity, and range.
| Feature | Passive RFID | Active RFID |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Powered by reader | Built-in battery |
| Data Capacity | 96–8,192 bits | 32 KB or more |
| Range | Up to 10 m | Up to 100 m |
| Lifespan | Unlimited (no battery) | Limited by battery life |
| Cost | <$0.10 per tag | $10–$50 per tag |
Which Should You Choose?
- Passive Tags: Ideal for inventory, retail, access control.
- Active Tags: Best for real-time asset tracking, logistics, IoT sensors.
Real-World Examples — What Data Is Stored on RFID Tags?
Let’s look at how RFID data storage works across real industries.
In Retail
- Product ID (EPC)
- Pricing, SKU, and lot numbers
- Shelf location or category data
In Healthcare
- Patient ID
- Medication dosage information
- Equipment tracking
In Logistics
- Shipment IDs, timestamps
- Container codes
- Route and checkpoint tracking
In Animal Tracking
- Breed ID, vaccine records
- GPS or location identifiers (in active tags)
Pro Insight: Most enterprise systems link tag IDs to cloud databases (ERP, WMS), reducing the need to store large datasets on the tag itself.
How Data Is Written to RFID Tags (Encoding Process)
Hardware Requirements
- RFID Writer or Reader/Writer Module
- Compatible Software (TagWriter, Arduino IDE, or SDKs)
- RFID-Compatible Tags
Typical Encoding Workflow
- Connect your writer to the system or microcontroller.
- Select the tag type and frequency (LF, HF, UHF).
- Choose data format (EPC, HEX, or ASCII).
- Write data to the tag using software commands.
- Verify data using a read function.
Common Encoding Formats
| Format | Example | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| EPC (96-bit) | 300833B2DDD9014000000001 | Product ID |
| HEX | 0xA1B2C3D4 | Binary data storage |
| ASCII | “ITEM00123” | Readable strings |
Need industrial-grade encoders? Browse our RFID writer kits for UHF and NFC systems.
RFID vs. Barcode vs. NFC: Data Storage Comparison
| Feature | RFID | Barcode | NFC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Capacity | 64 bits–32 KB | 12–20 characters | Up to 4 KB |
| Read Range | 1–100 m | 0.2–1 m | 0–10 cm |
| Rewritable? | Yes | No | Yes |
| Simultaneous Reads | 100s of tags | One at a time | One at a time |
| Durability | High | Low | Medium |
Key Takeaways
- RFID: Best for high-speed, high-volume data environments.
- Barcode: Simple and cheap for static IDs.
- NFC: Ideal for secure, short-range interactions (e.g., payments).
Thinking of upgrading from barcodes to RFID? Get a free implementation quote.
FAQs About RFID Data Storage
Can RFID tags be rewritten?
Yes — most HF and UHF tags support multiple write cycles until memory wear occurs.
How long does data remain on an RFID tag?
Up to 10 years or more for passive tags, depending on the chip quality.
Is RFID data encrypted?
Some tags support AES/DES encryption; others rely on password protection.
Can I program RFID tags with a smartphone?
Yes, if they are NFC-compatible (13.56 MHz) and your phone has an NFC reader.
What software is used to write to RFID tags?
TagWriter, Arduino IDE (with libraries), or manufacturer SDKs.
The Future of RFID Data Storage
The future of RFID lies at the intersection of IoT and AI — where tags don’t just store data but actively communicate with cloud systems and sensors.
Emerging Innovations
- Increased memory density with micro-EEPROM technology
- Integrated sensors that store temperature or motion data
- AI-driven RFID analytics to automate decision-making
- Blockchain-backed traceability for product authenticity
Conclusion: Summing It All Up
RFID tags are small but powerful data carriers that form the foundation of modern automation.
From basic memory structures to advanced encryption, understanding how RFID tags store and transmit data empowers engineers, developers, and businesses to build smarter, more secure systems.
Key Takeaways:
- Choose tag types based on range, capacity, and application.
- Use secure, password-protected encoding for sensitive data.
- Integrate RFID with backend systems for scalability.
Need help designing or programming your RFID system?
Contact our team for custom RFID solutions, hardware sourcing, and implementation support.

Ray Zhou
This article was written by Ray Zhou, an RFID technology expert with more than 10 years of industry experience.
Comments
Hot Products

RFID in Logistics: How to Eliminate RFID Misrouting and RFID Label Failures
RFID in logistics is more than just a tool to speed up processes. It has become a key part of how modern supply chains operate.

What Is RFID Waste Management
Imagine a city where every trash bin speaks — not literally — but through a tiny chip that tells the system when it’s full, when it’s emptied, and where it went. That’s what RFID waste management is doing today.

What are Bolt Seals and their Applications? | Complete Guide
In global trade and logistics, bolt seals play a crucial role in ensuring cargo security and compliance. These small but powerful devices are designed to lock shipping containers, trailers, and cargo doors with a tamper-evident mechanism.

What is an RFID Card Protector? Benefits, Use Cases, and Buying Guide
RFID technology (Radio Frequency Identification) is everywhere: in your credit cards, ID badges, transit passes, hotel room keys, and more. It offers speed and convenience, but it also opens the door to a new kind of digital theft called “skimming.” That’s where an RFID card protector comes in.

RFID Wristbands for Events: Bulk Buying Guide for Organizers
RFID wristbands for events are becoming the go-to solution for organizers who need faster entry, fraud prevention, and cashless payments at concerts, festivals, and sports venues. Unlike paper tickets or QR codes, these smart wristbands use embedded chips to streamline access, secure transactions, and improve the guest experience.

How RFID Tag on Windscreen Improves Vehicle Access Control and Toll Systems
In today’s fast-paced world, vehicle identification needs to be quick, secure, and contactless. An RFID Tag on the Windscreen provides exactly that — a reliable way to manage toll collection, parking, and gated access without stopping vehicles.
Tags
RELATED BLOGS

RFID in Logistics: How to Eliminate RFID Misrouting and RFID Label Failures
RFID in logistics is more than just a tool to speed up processes. It has become a key part of how modern supply chains operate.

What Is RFID Waste Management
Imagine a city where every trash bin speaks — not literally — but through a tiny chip that tells the system when it’s full, when it’s emptied, and where it went. That’s what RFID waste management is doing today.

What are Bolt Seals and their Applications? | Complete Guide
In global trade and logistics, bolt seals play a crucial role in ensuring cargo security and compliance. These small but powerful devices are designed to lock shipping containers, trailers, and cargo doors with a tamper-evident mechanism.




