
What is an RFID Tag?
Table of Contents
Introduction to RFID Technology
This article will delve deep into the world of RFID tags, exploring their functionality, types, applications, and their impact on our daily lives. Whether you’re a business owner looking to streamline operations or simply curious about this ubiquitous technology, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights into the fascinating world of RFID tags.
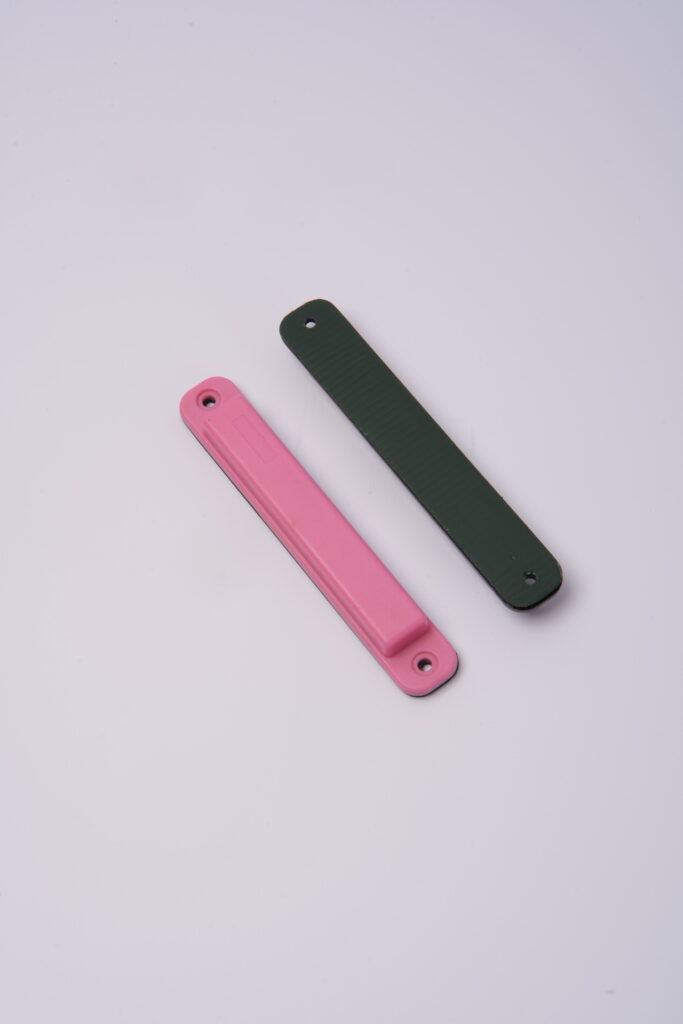

What Exactly is an RFID Tag and How Does it Work?
An RFID tag is a small electronic device that consists of a tiny chip and an antenna. These tags are designed to communicate with RFID readers using radio waves wirelessly. The primary function of an RFID tag is to store and transmit data, typically a unique identifier, that can be used to track or identify the item to which it’s attached. The basic components of an RFID tag include:
- Microchip: Stores and processes information
- Antenna: Receives and transmits signals
- Substrate: The material that holds the components together
RFID tags work on a simple principle: when an RFID reader emits a radio signal, the tag’s antenna picks up this signal and uses it to power the microchip. The chip then sends back a signal containing its stored information to the reader. This process happens almost instantaneously, allowing for quick and efficient data collection.RFID tags come in various forms and can be as small as a grain of rice or as large as a credit card. They can be embedded in products, attached to assets, or even implanted under the skin of animals for identification purposes.
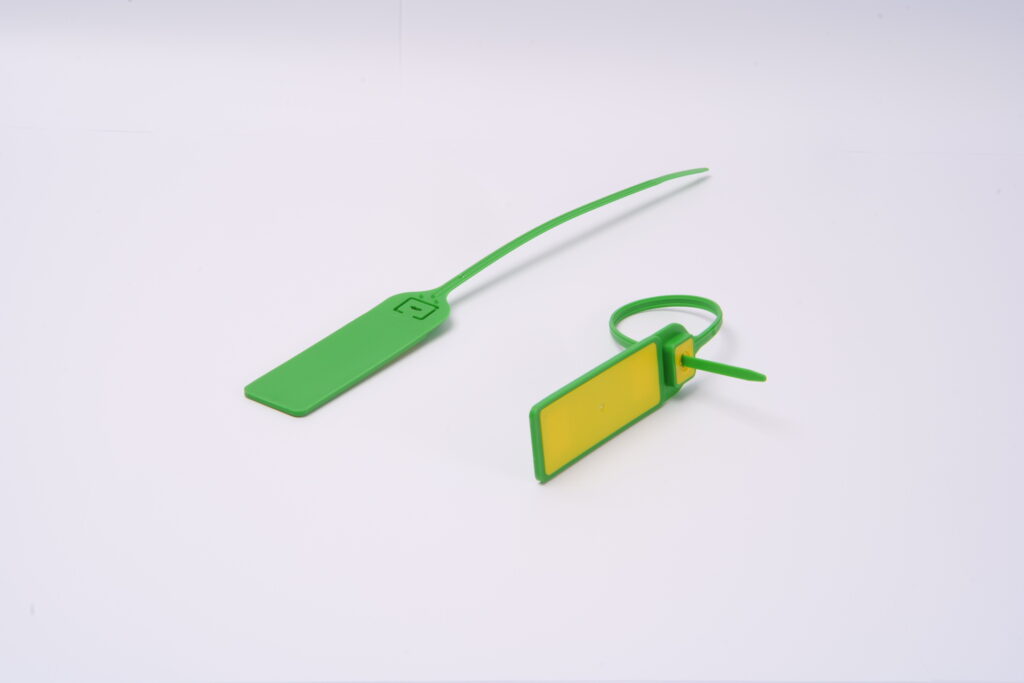

What are the Different Types of RFID Tags?
RFID tags are not one-size-fits-all solutions. They come in various types, each designed for specific applications and environments. Understanding these types is crucial for choosing the right RFID solution for your needs.
Active RFID Tags: The Long-Range Powerhouses
Active RFID tags are equipped with their power source, typically a battery. This allows them to actively broadcast their signal to readers, resulting in a much longer read range compared to passive tags. Key features of active RFID tags include:
- Read range up to 100 meters or more
- Ability to continuously transmit data
- Larger size due to the battery
- Higher cost compared to passive tags
- Ideal for tracking high-value assets or in large areas
Active tags are commonly used in applications such as vehicle tracking, asset management in large warehouses, and personnel tracking in high-security environments.
Passive RFID Tags: The Cost-Effective Workhorses
Passive RFID tags do not have their power source. Instead, they draw power from the RFID reader’s radio waves. While this limits their read range, it also makes them smaller, cheaper, and more durable. Characteristics of passive RFID tags include:
- Read range typically up to 10 meters
- Smaller and more flexible form factors
- Lower cost, making them suitable for high-volume applications
- Longer lifespan due to the absence of a battery
- Ideal for inventory tracking, supply chain management, and access control
Passive RFID tags are widely used in retail for inventory management, in libraries for book tracking, and in many access control systems.
Semi-Passive RFID Tags: The Best of Both Worlds?
Semi-passive RFID tags, also known as battery-assisted passive (BAP) tags, fall between active and passive tags. They have a battery to power the chip’s circuitry but rely on the reader to supply power for communication. This results in:
- Longer read range than passive tags, but shorter than active tags
- Longer battery life than active tags
- More reliable performance in challenging environments
- Higher cost than passive tags, but lower than active tags
Semi-passive tags are often used in sensor applications where real-time data logging is required, such as temperature monitoring in cold chain logistics.
RFID Frequency Ranges & What They Mean
Different RFID systems use different frequencies. Choosing the right one depends on read range, environment, and data volume.
| Frequency | Range | Common Uses |
| Low Frequency (LF) 125–134 kHz | <10 cm | Animal ID, key fobs |
| High Frequency (HF) 13.56 MHz | Up to 30 cm | Smart cards, library books, NFC |
| Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) 860–960 MHz | Up to 10m | Inventory, logistics, retail |
How Do RFID Tags Compare to Barcodes?
While both RFID tags and barcodes are used for identification and tracking, they have distinct differences:
- Line of Sight: Barcodes require a direct line of sight to be read, while RFID tags can be read without visual contact.
- Read Range: RFID tags can be read from a greater distance than barcodes.
- Simultaneous Reading: Multiple RFID tags can be read simultaneously, while barcodes must be scanned one at a time.
- Data Capacity: RFID tags can store more information than traditional barcodes.
- Durability: RFID tags are more durable and can withstand harsh environments better than printed barcodes.
- Cost: RFID tags are generally more expensive than barcodes, but offer more functionality.
What are the Most Common Applications of RFID Tags?
RFID technology has found its way into numerous industries and applications. Some of the most common uses include:
- Retail Inventory Management: RFID tags help retailers track inventory levels, reduce shrinkage, and improve supply chain efficiency.
- Supply Chain and Logistics: RFID tags enable real-time tracking of goods throughout the supply chain, from manufacturer to end consumer.
- Asset Tracking: Companies use RFID to keep track of valuable assets, equipment, and tools.
- Access Control: RFID-enabled cards or fobs are used for secure access to buildings and restricted areas.
- Animal Tracking: RFID microchips are implanted in pets and livestock for identification and tracking purposes.
- Healthcare: RFID is used for patient identification, medication tracking, and equipment management in hospitals.
- Automotive: RFID is used in car keys for keyless entry and ignition systems.
- Payment Systems: Some credit cards and mobile payment systems use RFID for contactless transactions.

What are the Key Benefits of Using RFID Tags?
The adoption of RFID technology offers numerous advantages across various industries:
- Improved Efficiency: RFID enables faster and more accurate data collection compared to manual methods or barcode scanning.
- Enhanced Visibility: Real-time tracking provides better visibility into inventory levels and asset locations.
- Increased Accuracy: RFID reduces human error in data collection and inventory management.
- Theft Prevention: RFID tags can help prevent theft and reduce shrinkage in retail environments.
- Improved Customer Experience: In retail, RFID can help ensure product availability and enable faster checkouts.
- Cost Savings: While initial implementation can be costly, RFID often leads to long-term cost savings through improved efficiency and reduced labor costs.
- Data Analytics: The data collected through RFID systems can provide valuable insights for business decision-making.
What are the Challenges and Limitations of RFID Technology?
While RFID offers many benefits, it’s important to be aware of its limitations and challenges:
- Cost: RFID systems can be expensive to implement, especially for small businesses.
- Technical Issues: Metal and liquids can interfere with RFID signals, affecting read accuracy.
- Standardization: Different RFID standards can lead to compatibility issues.
- Privacy Concerns: The ability to read RFID tags without a line of sight has raised privacy concerns.
- Security Risks: RFID systems can be vulnerable to hacking and unauthorized access if not properly secured.
- Read Range Limitations: Passive RFID tags have a limited read range, which may not be suitable for all applications.
How Do You Choose the Right RFID Tag for Your Needs?
Selecting the appropriate RFID tag depends on several factors:
- Application: Consider what you’re tagging and how it will be used.
- Environment: Factors like temperature, moisture, and the presence of metal can affect tag performance.
- Read Range: Determine how far the tag needs to be read from.
- Data Storage: Consider how much data needs to be stored on the tag.
- Frequency: Choose between low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), or ultra-high frequency (UHF) based on your needs.
- Form Factor: Tags come in various shapes and sizes, from labels to hard tags.
- Cost: Balance the cost of the tags with your budget and the value of the items being tagged.
What Does the Future Hold for RFID Technology?
The future of RFID technology looks promising, with several exciting developments on the horizon:
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: RFID is expected to play a crucial role in the growing IoT ecosystem.
- Improved Sensors: RFID tags with advanced sensing capabilities for temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors.
- Enhanced Security: Development of more secure RFID protocols to address privacy and security concerns.
- Smaller and Cheaper Tags: Advancements in manufacturing are likely to result in even smaller and more cost-effective RFID tags.
- Biodegradable Tags: Research is ongoing to develop environmentally friendly, biodegradable RFID tags.
- Increased Read Ranges: Improvements in antenna design and power management may lead to longer read ranges for passive tags.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Combining RFID data with AI could lead to more intelligent and predictive systems.
How Can Businesses Implement RFID Technology Successfully?
Implementing RFID technology requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key steps for a successful RFID implementation:
- Define Clear Objectives: Identify specific goals for your RFID implementation.
- Conduct a Feasibility Study: Assess the technical and financial viability of RFID for your business.
- Choose the Right Solution: Select appropriate hardware and software based on your needs.
- Plan for Integration: Ensure the RFID system can integrate with your existing IT infrastructure.
- Train Your Staff: Provide comprehensive training to employees who will be using the RFID system.
- Start with a Pilot Project: Test the system on a small scale before full implementation.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor the system’s performance and make necessary adjustments.
What are Some Innovative Uses of RFID Tags?
While RFID is widely used in inventory and asset tracking, innovative applications are constantly emerging:
- Smart Packaging: RFID tags in packaging can provide consumers with product information, authenticity verification, and even interactive experiences.
- Wearable Technology: RFID is being integrated into clothing and accessories for various applications, from fitness tracking to contactless payments.
- Smart Cities: RFID is used in waste management systems, public transportation, and parking management in smart city initiatives.
- Agriculture: RFID tags help in tracking livestock, monitoring crop growth, and managing farm equipment.
- Sports and Events: RFID is used for timing in races, crowd management at events, and even interactive fan experiences.
- Museum and Art Galleries: RFID enables interactive exhibits and helps in tracking and authenticating valuable artworks.
- Library Management: Many libraries use RFID for self-checkout systems and inventory management.
What are Some Innovative Uses of RFID Tags?
What’s the difference between an RFID tag and a barcode?
RFID uses radio waves, where as barcodes require a line of sight. RFID can scan hundreds of items in seconds, barcodes can’t.
Can RFID tags be reused?
Some RFID tags (especially HF and UHF types) can be rewritten or reused, depending on the chip type and system compatibility.
Do RFID tags work on metal or liquid surfaces?
Standard RFID tags may struggle near metal or liquid, but on-metal RFID tags are specifically designed to perform well on these challenging surfaces.
Is RFID safe for humans and pets?
Yes. RFID uses low-power radio waves and is considered safe for use around humans and animals. It’s even used in pet microchipping and hospital wristbands.
Ready to Use RFID Tags in Your Project?
At JIA RFID, we offer a wide range of custom RFID tags, including:
- On-metal tags
- UHF logistics labels
- Anti-counterfeit smart tags
- Waterproof, heat-resistant designs
Contact us to get a quote or explore our RFID product catalog for your specific needs.
In conclusion, RFID tags have become an integral part of our increasingly connected world. From streamlining supply chains to enhancing security and enabling innovative consumer experiences, the applications of RFID technology are vast and continue to grow. As the technology evolves, we can expect to see even more creative and efficient uses of RFID tags across various industries.
Comments
Hot Products

RFID in Logistics: How to Eliminate RFID Misrouting and RFID Label Failures
RFID in logistics is more than just a tool to speed up processes. It has become a key part of how modern supply chains operate.

What Is RFID Waste Management
Imagine a city where every trash bin speaks — not literally — but through a tiny chip that tells the system when it’s full, when it’s emptied, and where it went. That’s what RFID waste management is doing today.

What are Bolt Seals and their Applications? | Complete Guide
In global trade and logistics, bolt seals play a crucial role in ensuring cargo security and compliance. These small but powerful devices are designed to lock shipping containers, trailers, and cargo doors with a tamper-evident mechanism.

What is an RFID Card Protector? Benefits, Use Cases, and Buying Guide
RFID technology (Radio Frequency Identification) is everywhere: in your credit cards, ID badges, transit passes, hotel room keys, and more. It offers speed and convenience, but it also opens the door to a new kind of digital theft called “skimming.” That’s where an RFID card protector comes in.

RFID Wristbands for Events: Bulk Buying Guide for Organizers
RFID wristbands for events are becoming the go-to solution for organizers who need faster entry, fraud prevention, and cashless payments at concerts, festivals, and sports venues. Unlike paper tickets or QR codes, these smart wristbands use embedded chips to streamline access, secure transactions, and improve the guest experience.

How RFID Tag on Windscreen Improves Vehicle Access Control and Toll Systems
In today’s fast-paced world, vehicle identification needs to be quick, secure, and contactless. An RFID Tag on the Windscreen provides exactly that — a reliable way to manage toll collection, parking, and gated access without stopping vehicles.
Tags
RELATED BLOGS

RFID in Logistics: How to Eliminate RFID Misrouting and RFID Label Failures
RFID in logistics is more than just a tool to speed up processes. It has become a key part of how modern supply chains operate.

What Is RFID Waste Management
Imagine a city where every trash bin speaks — not literally — but through a tiny chip that tells the system when it’s full, when it’s emptied, and where it went. That’s what RFID waste management is doing today.

What are Bolt Seals and their Applications? | Complete Guide
In global trade and logistics, bolt seals play a crucial role in ensuring cargo security and compliance. These small but powerful devices are designed to lock shipping containers, trailers, and cargo doors with a tamper-evident mechanism.




