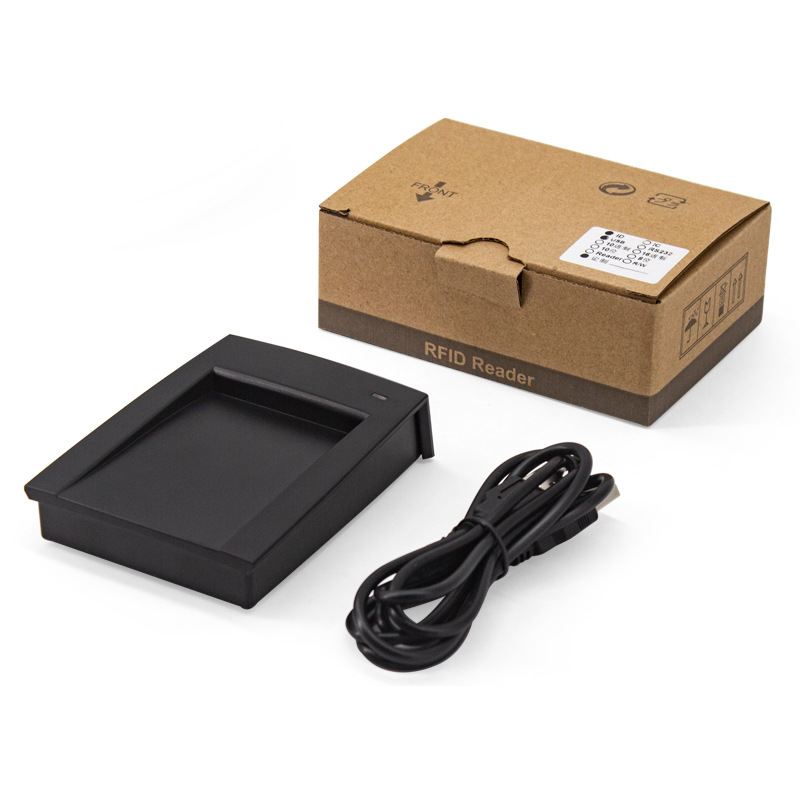
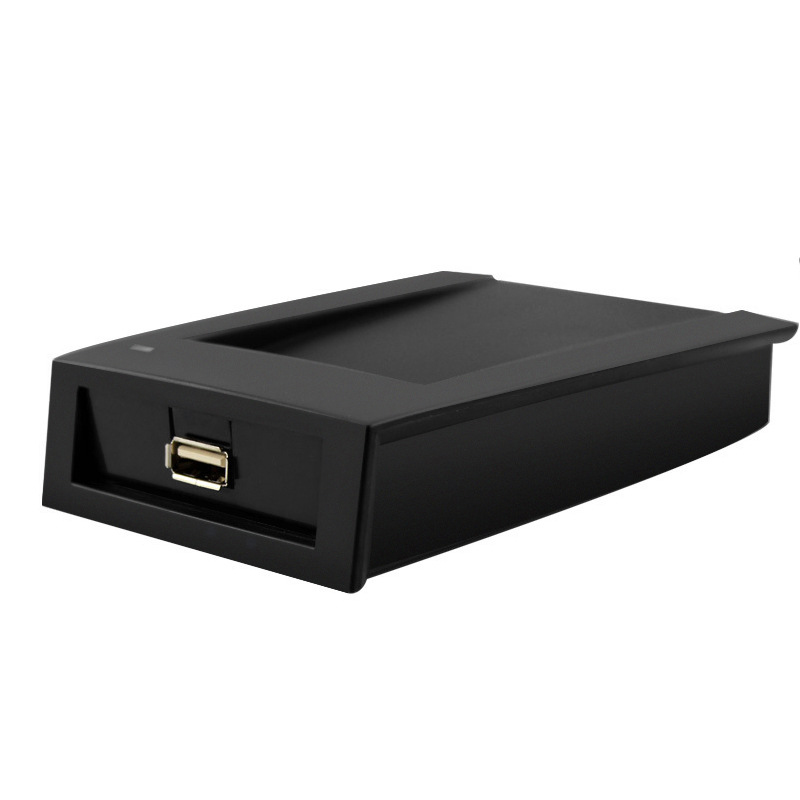
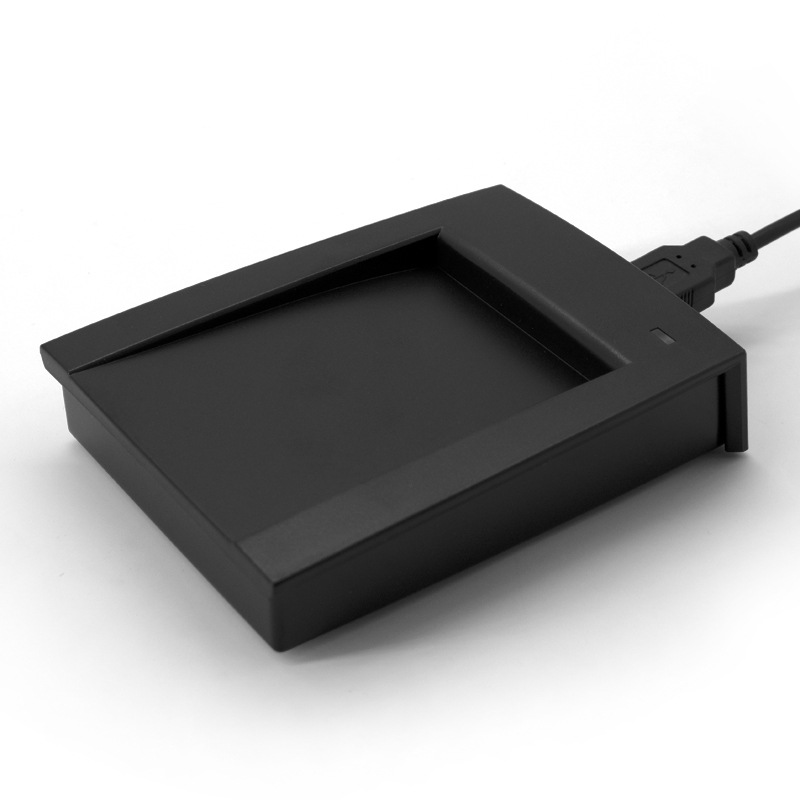
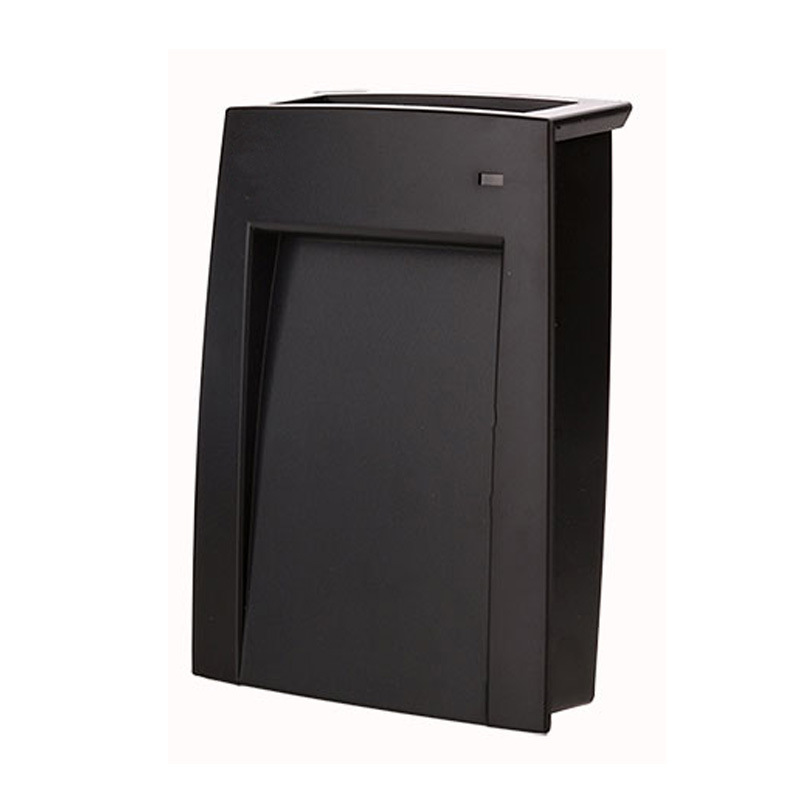
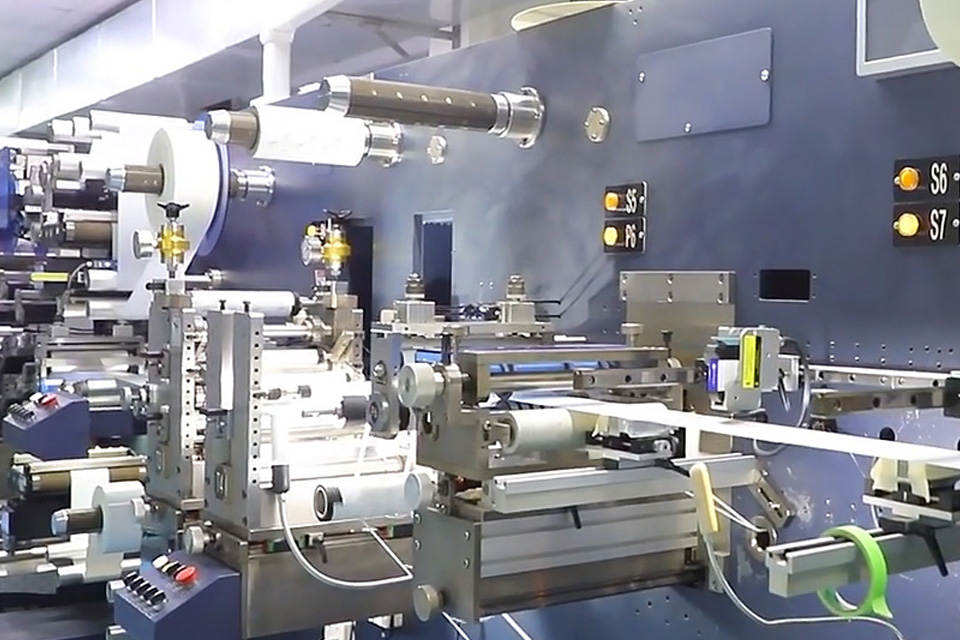
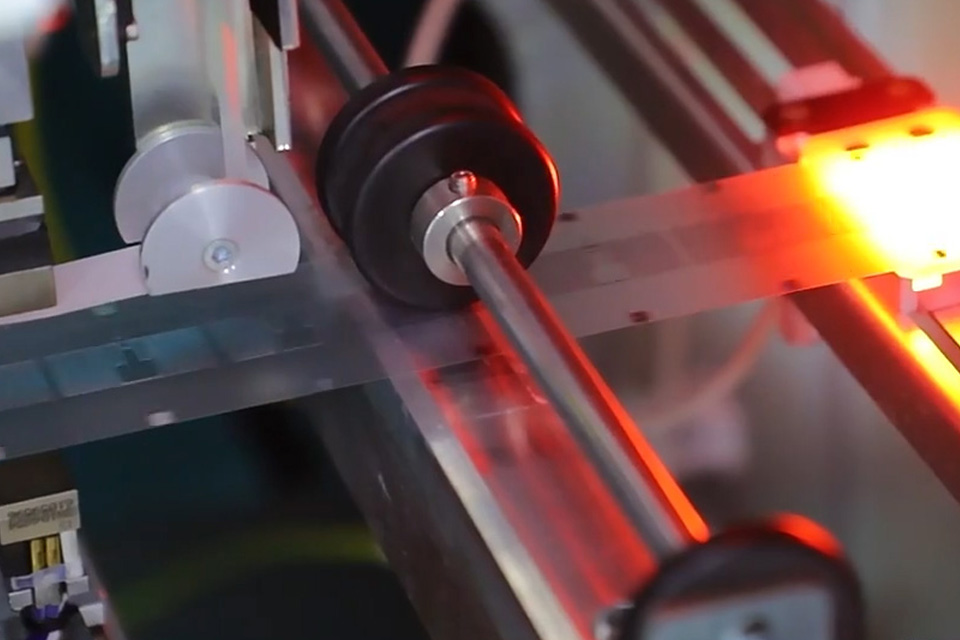
Desktop LF 134.2Khz RFID Reader with HDX+FDX RS232/485
134.2KHz RFID Reader: Desktop LF RFID Reader for Reliable Tag Scanning
The Desktop 134.2KHz RFID Reader is a compact and high-performance LF RFID reader optimized for animal tracking, access control, and industrial data collection. Supporting both HDX and FDX protocols (ISO11784/11785), this reader ensures accurate tag reading in real-time, even near metallic or wet environments.
Perfect for desktop or wall-mount use, it integrates seamlessly with RS232/RS485/USB interfaces and supports a variety of LF RFID tags like EM4200 and T5577. The rugged construction, ESD protection, and development-friendly SDK make it ideal for long-term deployment in field and indoor environments.
Applications of 134.2KHz RFID Reader
- Animal Identification (livestock, pets, wildlife research)
- Industrial Access Control (factory entry systems)
- Agricultural Automation (automatic feeding or weighing)
- Healthcare (asset tracking, patient ID verification)
- Lab Testing (sample verification & tagging)
Key Features & Benefits
| Feature | Description |
| Frequency Range | 125KHz / 134.2KHz (LF) |
| Protocol Support | ISO11784 / ISO11785 (FDX-B, HDX) |
| Read Distance | Up to 50cm (depending on tag and environment) |
| Communication Interfaces | USB, RS232, RS485, UART |
| Chip Compatibility | EM4200, T5577, TK4100 |
| Output Formats | Decimal & Hexadecimal |
| SDK & Integration | Free SDK, Serial Port Emulation, Keyboard Emulation |
| Mounting Options | Desktop or wall mount |
| Certifications | FCC / CE |
| Durability | ESD-protected; supports industrial temperature range (-25°C ~ 75°C) |
Why Choose Our 134.2KHz RFID Reader?
- HDX + FDX-B Dual Mode – Full ISO11784/85 support
- Desktop Friendly – Sleek design for lab, vet office, or desktop use
- Versatile Communication – USB, RS232/485, and UART support
- High Compatibility – Works with EM4200, T5577, and more
- Developer Ready – Comes with SDK and protocol docs
- Certified – FCC and CE-approved for industrial use
Looking for a reliable 134.2KHz RFID Reader for your RFID system
Contact our sales team today for technical specs, OEM pricing, and custom integration support.
Request a free sample or developer SDK to start integrating this reader into your system.
Frequently Asked Question
The top questions about 134.2Khz RFID Reader.
A 134.2KHz RFID reader is used in low-frequency RFID systems for applications like animal identification, access control, and industrial data collection. It supports both HDX and FDX-B tag types per ISO11784/11785 standards.
It supports EM4200, T5577, TK4100, and other 125KHz/134.2KHz compatible RFID tags.
It can read up to 50 cm depending on the tag and environmental conditions, including interference from metal or liquids.
Yes. It includes a free SDK, along with serial port emulation, USB keyboard emulation, and API docs for integration.
Absolutely. It’s designed to support animal ID applications including livestock tagging, pet microchip scanning, and wildlife research.
Hot To Customize RFID Tags
Know the customization process about RFID tags
Size & Shape
Send your requirements on size and shapes. Tags are typically designed in simple shapes and sizes to match the internal antenna. However, they can also be customized in various sizes and shapes to best fit the intended application and the asset being tagged. For instance, RFID hang tags can be customized in size, shape, and attachment method to perfectly suit specific applications.
Layout & Chips
In the label format designer, select the layout that matches the type and size of the RFID label you wish to create. Our factory provides a variety of label templates, including RFID-specific options. We also offer a range of RFID chips tailored to meet your specific requirements.

High Customization
Custom tags are designed from the ground up to meet the needs of specific applications, with unique variables for nearly every option listed below. A semi-custom tag typically starts as a standard tag but offers additional customization options, such as custom printing, encoding, or specific backings and attachment methods.

Sample Confirmation
Before proceeding with full-scale production, we offer a sample confirmation process to ensure that the RFID tags meet your exact specifications and application requirements.

Mass Production
Our mass production process for RFID tags is designed to deliver high-quality, reliable products at scale, ensuring that your business has a steady and consistent supply of RFID solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities and advanced technology, we maintain efficiency and precision throughout the production cycle.
RFID Tags Application
Use customized RFID tags in different industies.

RFID Vehicle Tags
Vehicles with RFID tags enable secure access to gated areas. RFID tags also streamline truck weighing for efficient billing.

Temperature Sensor Tags
RFID temperature sensors, used in industries like steel, send data to alert users of unsafe conditions via RFID readers.
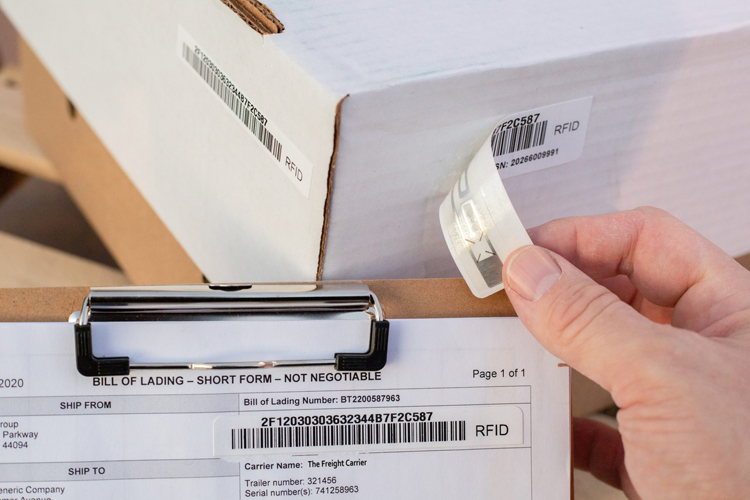

RFID Supply Chain Tags
RFID tags for supply chain visibility track products, showing when a box, pallet, or container moves from one facility to another.
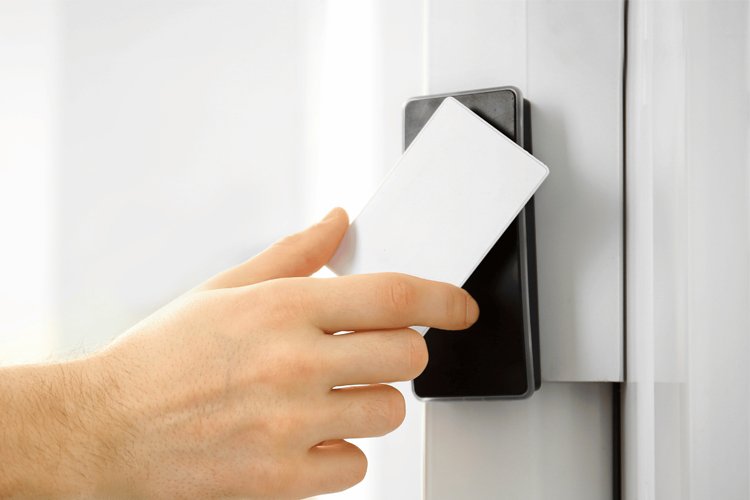

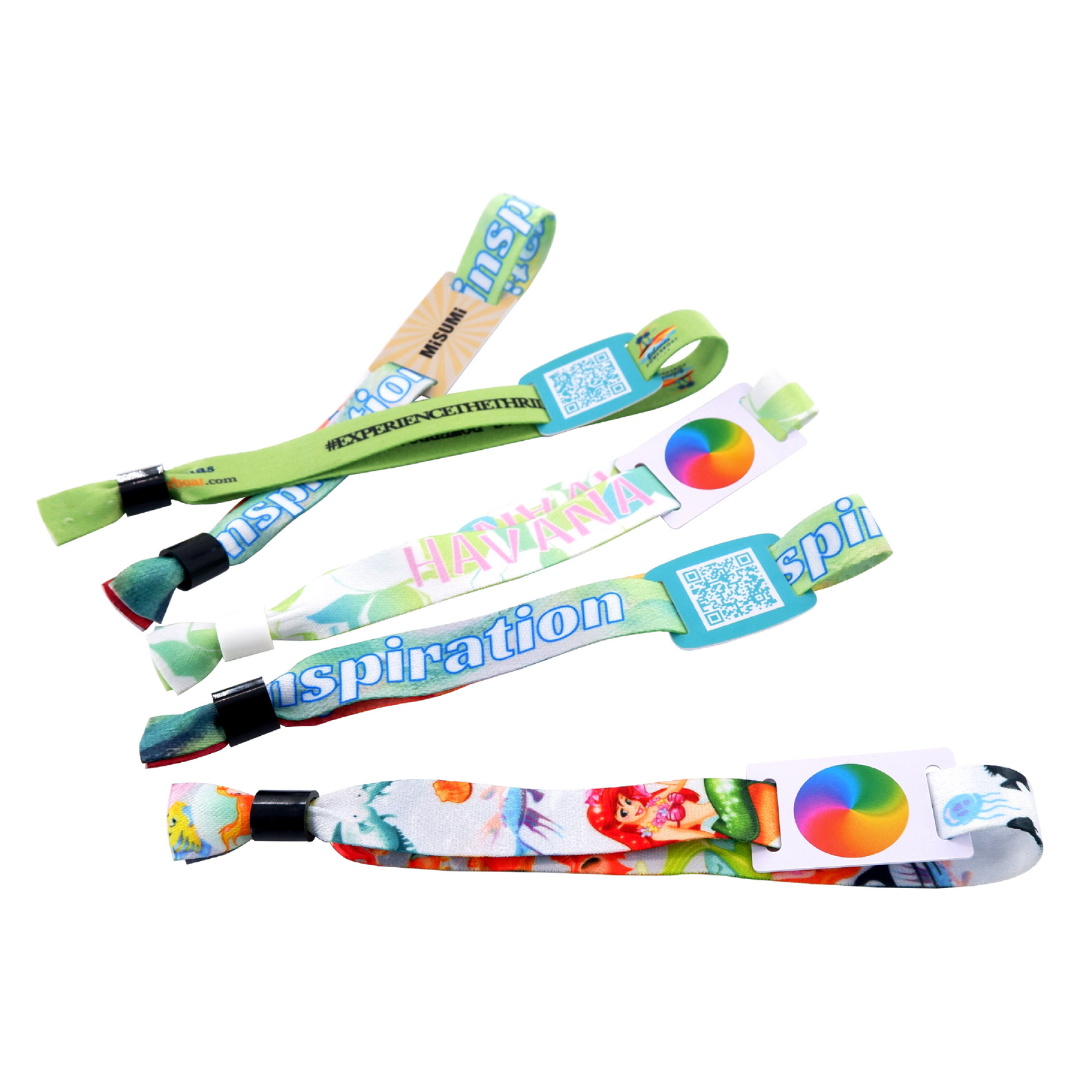
RFID Personnel Tracking
RFID strengthens access security: employee badges for workspace entry, hotel wristbands for pool access.
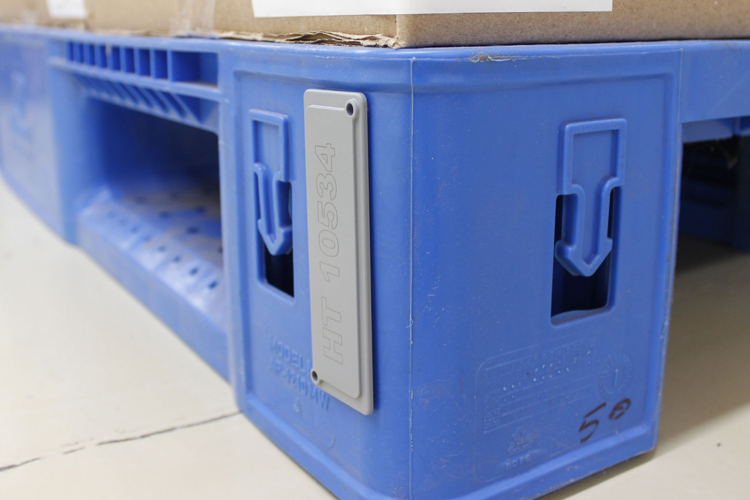

RFID Pallet Tracking Tags
Our RFID tags are ideal for tracking pallets and containers, offering durable, low-profile solutions for warehouse management.
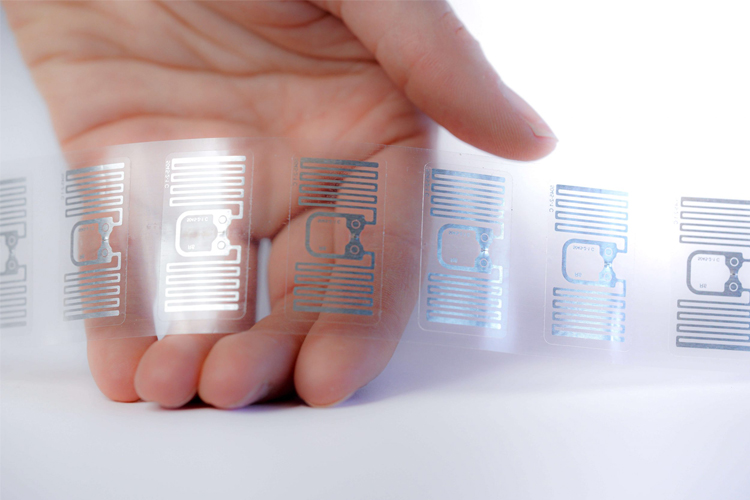

Custom RFID Tags & Labels
Our factory supplies custom RFID tags and OEM hardware solutions for unique needs when standard RFID products aren't available.
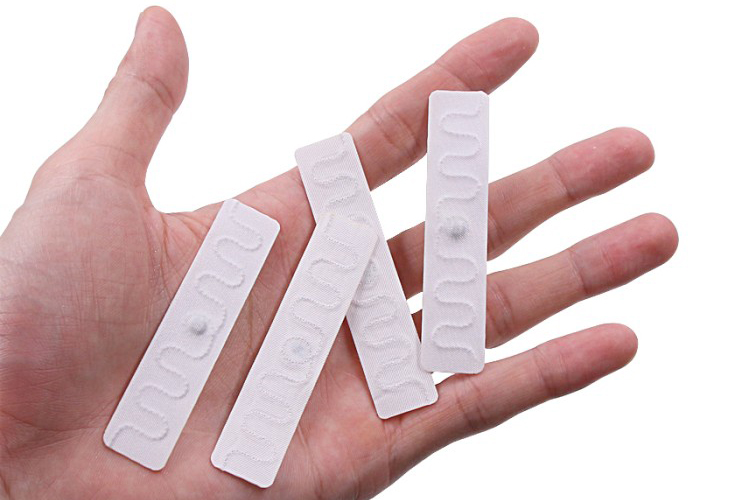

RFID Laundry Tags
Our RFID laundry tags, with a soft rubber casing, are flexible and durable, surviving 200 wash cycles and 60 bars of pressure.
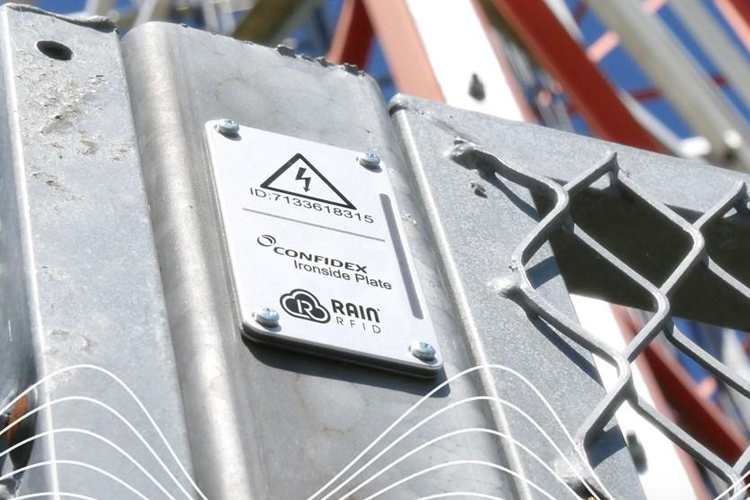

Industrial RFID Tags
We provide rugged industrial RFID tags and readers for demanding applications. Our tags withstand all weather conditions.
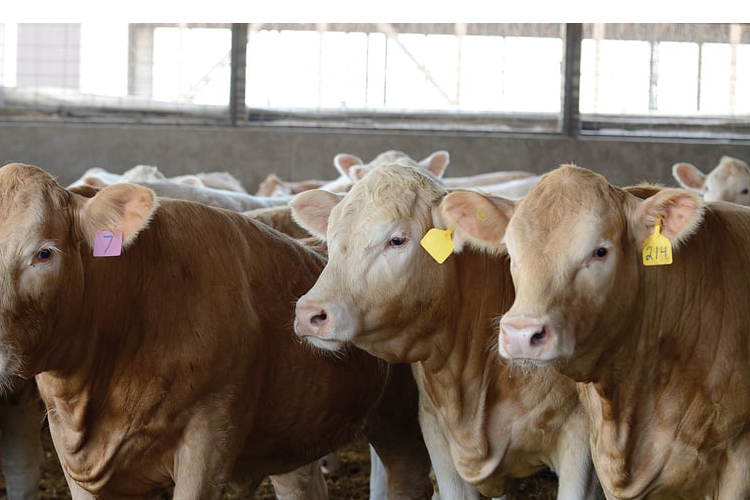

Animal RFID Tags
RFID tags track animals and pets using ear tags or injectable ampoules. Ear tags can be custom-printed and come in various colors.
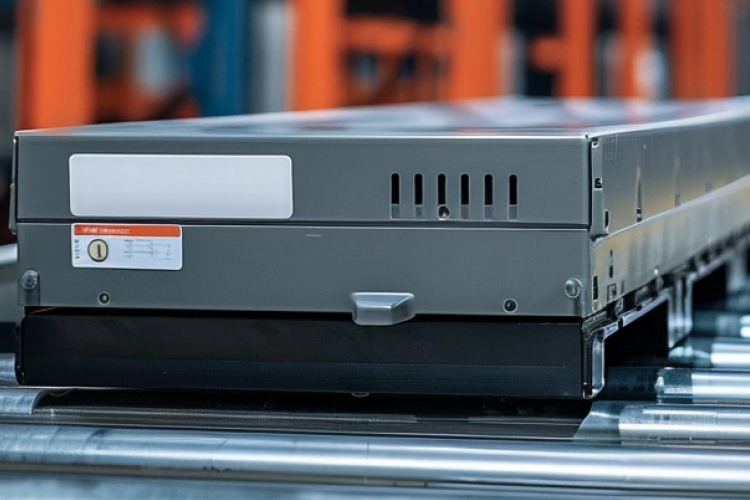

RFID Asset Tracking
RFID tags for asset tracking, like file servers, rental equipment, streamline inventory, asset management, enabling quick location, tracking.
Consumables RFID Tags
RFID counterfeit tags on consumables, with a reader in the machine, verify authenticity and prevent counterfeit use.
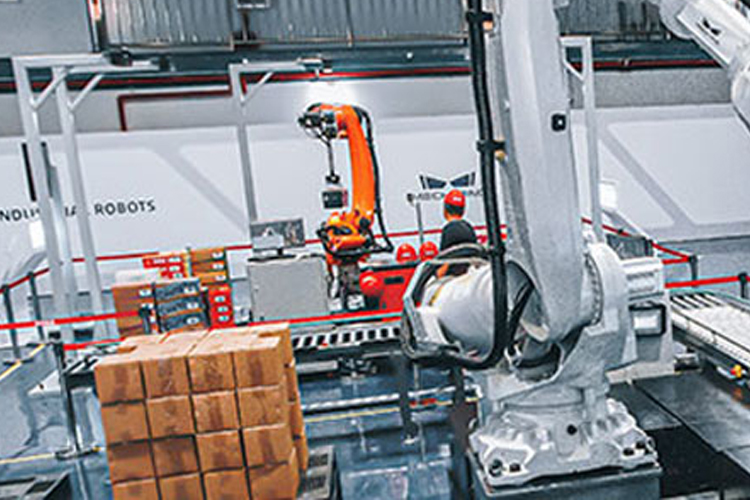

Manufacturing RFID Systems
RFID tags are used on almost all products—apparel, furniture, appliances, and cars—and are crucial for automated manufacturing systems.
Why Choose Us
As an original manufacturer with over 13 years of experience, we specialize in designing and manufacturing passive RFID (NFC, HF, and UHF) tags for applications in inventory, laundry, access control, identification, and industrial automation management.
We are a pioneering leader in RFID technology and smart product solutions. For nearly 20 years, we have been at the forefront of custom RFID and NFC technology, offering innovative solutions in every imaginable form. Our expertise lies in developing and producing RFID/NFC products that are tailored to meet your specific requirements.
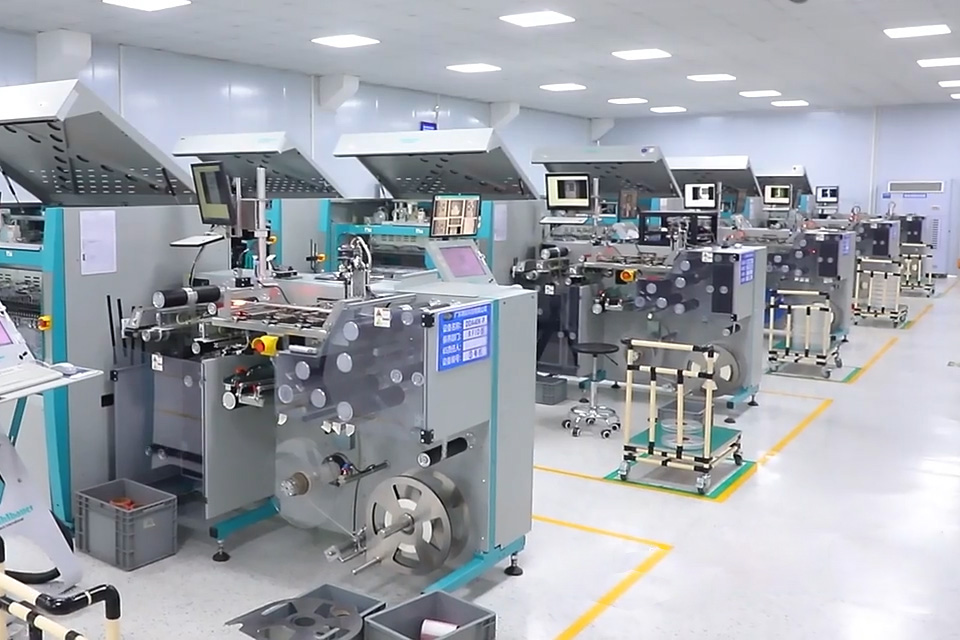

As the world’s leading RFID supplier, our factory is passionate about RFID technology. We deliver a wide range of products, including NFC tags, NFC cards, RFID/NFC labels, RFID inlays, various apparel tags, laundry tags, and RFID devices, to clients around the globe. Our RFID products are widely used in marketing campaigns, healthcare monitoring, workforce management, stock control, access control, apparel systems, laundry systems, inventory systems, IoT systems, and security applications.
Our Benefits
We provide products with competitive pricing and reliable quality, backed by an after-sales warranty. Whether you are a distributor, system integrator, or end-user, you will find the right RFID and related products here, ensuring that your company gains tangible benefits.
We have grown into a company with over 200 team members, including a production department, R&D center, sales department, technical support, and after-sales service. Understanding that time is of the essence, we can fulfill customized orders within just 5 days. Our dedicated team of over 100 factory staff ensures a stable supply and fast delivery for all our orders.
Related Products
Customize any types RFID tags from our factory to meet your own requirements.